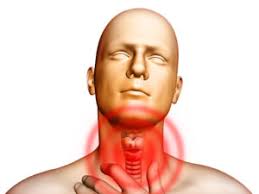
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN) is a rare neurological condition characterized by severe, recurring pain in the throat, tongue, ear, and tonsils. This condition affects the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), which is responsible for sensation in these areas.
Causes of Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Several factors can contribute to glossopharyngeal neuralgia, including:
- Nerve Compression: Blood vessels pressing against the glossopharyngeal nerve can trigger pain episodes.
- Tumors: Growths near the nerve can irritate or compress it.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Demyelination in multiple sclerosis patients can result in GPN.
- Throat or Neck Surgery: Injury to the nerve during surgical procedures may lead to this condition.
Symptoms of Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Symptoms often occur in sudden, intense bursts and may last for seconds to a few minutes. Key symptoms include:
- Sharp, stabbing pain in the throat, tongue, ear, or tonsil region
- Pain triggered by swallowing, speaking, coughing, or chewing
- Episodes that may become more frequent over time
Diagnosis of Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Diagnosing GPN involves:
- Medical History Review: Understanding the nature of pain and its triggers.
- Physical Examination: Identifying pain points through touch and movement tests.
- MRI or CT Scan: Imaging to detect nerve compression or tumors.
- Nerve Block Test: Injection to temporarily relieve pain, confirming GPN diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
1. Medications
- Anticonvulsants: Drugs like carbamazepine and gabapentin help control nerve pain.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants can alleviate chronic pain.
- Muscle Relaxants: Baclofen is sometimes prescribed for pain relief.
2. Surgical Interventions
- Microvascular Decompression (MVD): This procedure relieves nerve pressure by repositioning or removing blood vessels.
- Rhizotomy: Selective nerve severing to reduce pain signals.
3. Other Therapies
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Uses heat to disable pain-causing nerve fibers.
- Nerve Stimulation: Devices implanted under the skin can regulate nerve activity.
Lifestyle and Coping Strategies
- Diet Adjustments: Soft, easy-to-swallow foods can reduce pain episodes.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga and meditation may minimize pain triggers.
- Regular Follow-ups: Ongoing consultation with healthcare providers is crucial for symptom management.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What triggers glossopharyngeal neuralgia attacks?
Common triggers include swallowing, talking, yawning, coughing, or consuming cold foods or drinks.
2. Is glossopharyngeal neuralgia life-threatening?
While not life-threatening, severe pain episodes can significantly impact quality of life.
3. Can glossopharyngeal neuralgia be cured?
In some cases, surgical treatments like microvascular decompression can provide long-term relief.
4. How long do glossopharyngeal neuralgia episodes last?
Pain episodes may last from a few seconds to several minutes, with frequency varying among patients.
5. What is the success rate of microvascular decompression for GPN?
MVD has a high success rate, with many patients experiencing significant or complete pain relief.