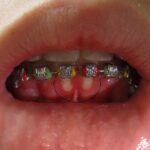
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease (periodontal disease) that causes irritation, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of the gingiva, the part of your gum around the base of your teeth. It is a reversible condition but can lead to more severe gum disease if left untreated.
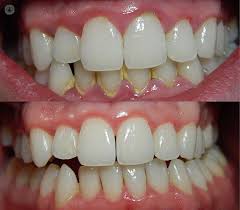
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, which encourages plaque formation. Plaque is a sticky, invisible film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth.
Common Causes
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking weakens the immune system, making gums more susceptible.
- Poor Nutrition: Vitamin deficiencies, especially Vitamin C, increase the risk.
- Dry Mouth Conditions: Reduced saliva flow promotes bacterial growth.
- Medications: Certain drugs reduce saliva or cause gum overgrowth.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause increase gum sensitivity.
- Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer affect gum health.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Identifying the early signs of gingivitis can help prevent progression to more serious conditions like periodontitis.
Common Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or puffy gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Tender or painful gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums
Diagnosis of Gingivitis
Dentists diagnose gingivitis by:
- Reviewing your dental and medical history
- Examining your teeth, gums, and tongue
- Measuring pocket depths with a periodontal probe
- Conducting dental X-rays if bone loss is suspected
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
Prompt treatment can reverse gingivitis and restore gum health. Treatment typically includes:
Professional Cleaning
- Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning): Removes plaque and tartar buildup beneath the gumline.
- Laser Treatment: May be recommended for severe cases to remove infected tissue.
Medications
- Antiseptic Mouthwashes: Reduce bacterial growth.
- Antibiotic Gels or Rinses: Control bacterial infection in deeper gum pockets.
Improved Oral Hygiene Practices
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing at least once daily
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash
Prevention of Gingivitis
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is key to preventing gingivitis. Follow these preventive measures:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly at least twice daily
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque
- Schedule regular dental checkups and professional cleanings
- Maintain a healthy diet to support gum health
- Avoid tobacco products
Complications of Untreated Gingivitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease that may lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis can also increase the risk of systemic health conditions such as:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory infections
- Pregnancy complications
Home Remedies for Gingivitis
While professional dental care is essential, some home remedies can support recovery:
- Saltwater Rinse: Reduces inflammation and bacteria.
- Oil Pulling: Swishing coconut or sesame oil may improve oral hygiene.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Turmeric Paste: Natural antibacterial properties promote healing.
When to See a Dentist
Visit your dentist if you experience:
- Persistent gum bleeding
- Pain while chewing
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Receding gums
FAQs:
How long does it take to reverse gingivitis?
With proper care and treatment, mild gingivitis can improve within 10-14 days. Severe cases may require more time.
Can gingivitis be cured permanently?
Yes, gingivitis can be fully reversed if treated promptly. However, ongoing oral hygiene is necessary to prevent recurrence.
What foods help improve gum health?
Foods rich in Vitamin C, calcium, and antioxidants, such as leafy greens, citrus fruits, and nuts, promote gum health.
Is gingivitis contagious?
While gingivitis itself is not contagious, the bacteria causing it can spread through saliva.
Can stress worsen gingivitis?
Yes, stress weakens the immune system and increases the risk of gum inflammation.
Gingivitis is a preventable and treatable condition that requires consistent oral care and professional dental visits. Early intervention can prevent severe gum disease, ensuring long-term oral health.