Genitourinary tract infections (GUTIs) are a common health concern affecting both men and women. These infections involve the urinary tract and reproductive organs, resulting in various complications if untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for effective management.
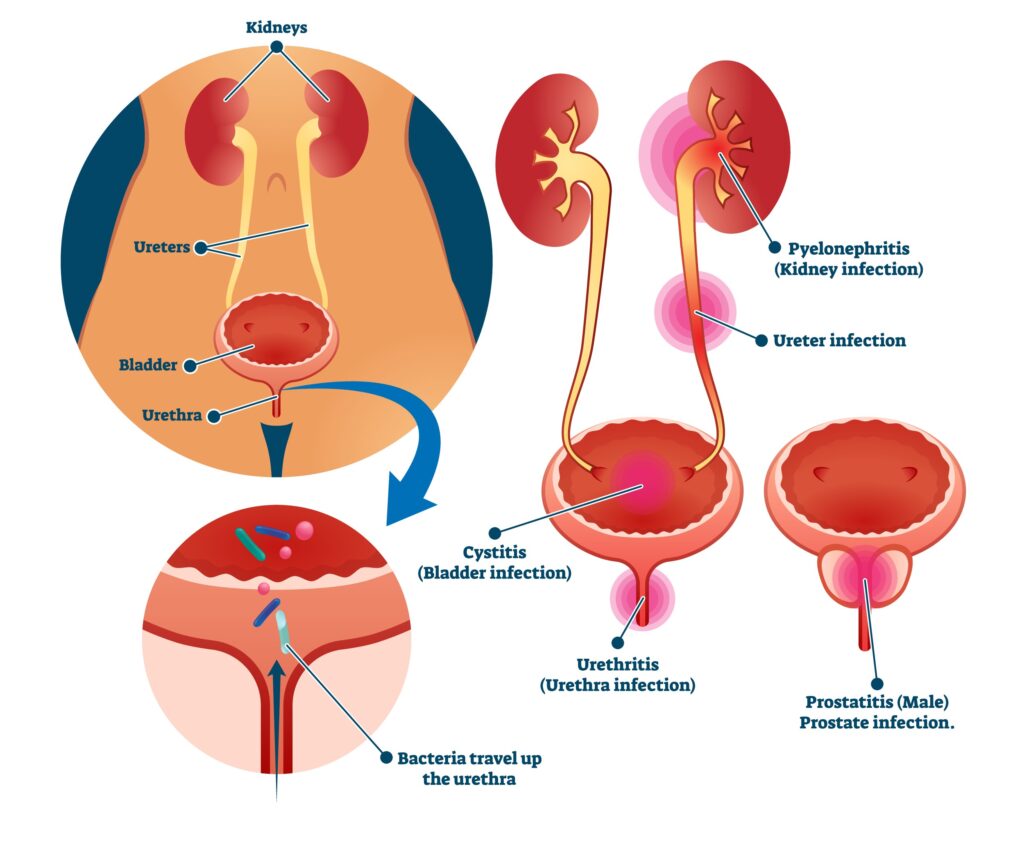
Causes of Genitourinary Tract Infections
GUTIs arise from bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. The most common bacterial pathogens include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis. Other contributing factors include:
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate genital care increases bacterial buildup.
- Sexual Activity: Unprotected intercourse can introduce pathogens.
- Urinary Retention: Incomplete bladder emptying fosters bacterial growth.
- Catheter Use: Prolonged use of urinary catheters raises infection risks.
- Weakened Immune System: Immunocompromised individuals are more susceptible.
Common Symptoms of Genitourinary Tract Infections
The symptoms of GUTIs vary based on the affected area:
Urinary Tract Symptoms
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic or abdominal discomfort
Genital Tract Symptoms
- Unusual discharge
- Itching, irritation, or redness
- Pain during intercourse
- Genital sores or ulcers
Diagnosis of Genitourinary Tract Infections
Accurate diagnosis requires a combination of clinical assessment and laboratory tests:
- Urinalysis: Detects white blood cells, bacteria, and nitrates.
- Urine Culture: Identifies the causative bacteria and antibiotic sensitivity.
- Blood Tests: Determines infection severity.
- Ultrasound or CT Scans: Identifies structural abnormalities.
- STD Testing: Essential for ruling out sexually transmitted infections.
Treatment Options for Genitourinary Tract Infections
Treatment varies depending on the infection’s cause and severity:
Antibiotic Therapy
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: Effective for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Ciprofloxacin: Preferred for severe bacterial GUTIs.
- Doxycycline or Azithromycin: Recommended for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Antifungal Medications
- Fluconazole: Treats fungal-based GUTIs.
Antiviral Drugs
- Acyclovir: Used for herpes-related GUTIs.
Home Remedies and Preventive Care
- Increase fluid intake to flush bacteria.
- Practice proper genital hygiene.
- Urinate after sexual activity to reduce bacterial transmission.
- Wear breathable, cotton underwear to minimize moisture buildup.
Complications of Untreated Genitourinary Tract Infections
If left untreated, GUTIs can lead to severe complications such as:
- Kidney Infections (Pyelonephritis)
- Bladder Inflammation (Cystitis)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Infertility
- Sepsis, which may become life-threatening
Prevention Strategies for Genitourinary Tract Infections
Prevention measures are crucial for reducing GUTI risks. Effective strategies include:
- Drinking ample water daily
- Practicing safe sex and using condoms
- Maintaining regular medical checkups
- Avoiding excessive douching or irritants
Genitourinary tract infections are prevalent but manageable conditions. Timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive care can effectively reduce complications. Individuals experiencing symptoms should consult healthcare providers for accurate assessment and intervention.
FAQs
1. What are the primary causes of genitourinary tract infections?
Bacterial pathogens like E. coli, poor hygiene, and unprotected intercourse are common causes.
2. How can genitourinary tract infections be prevented?
Preventive measures include proper hygiene, hydration, and practicing safe sex.
3. Are genitourinary tract infections contagious?
Certain infections, such as those caused by STIs, can be transmitted through sexual contact.
4. What are the best treatments for GUTIs?
Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals are common treatments depending on the infection’s cause.
5. When should I seek medical attention for GUTI symptoms?
Consult a doctor if symptoms persist beyond 48 hours or worsen despite home remedies.