Back pain is a pervasive condition affecting people of all ages, significantly impacting quality of life. From acute discomfort to chronic issues, back pain can arise from various causes and requires targeted strategies for prevention and treatment. This article explores the types, causes, symptoms, and advanced treatment options available for back pain.
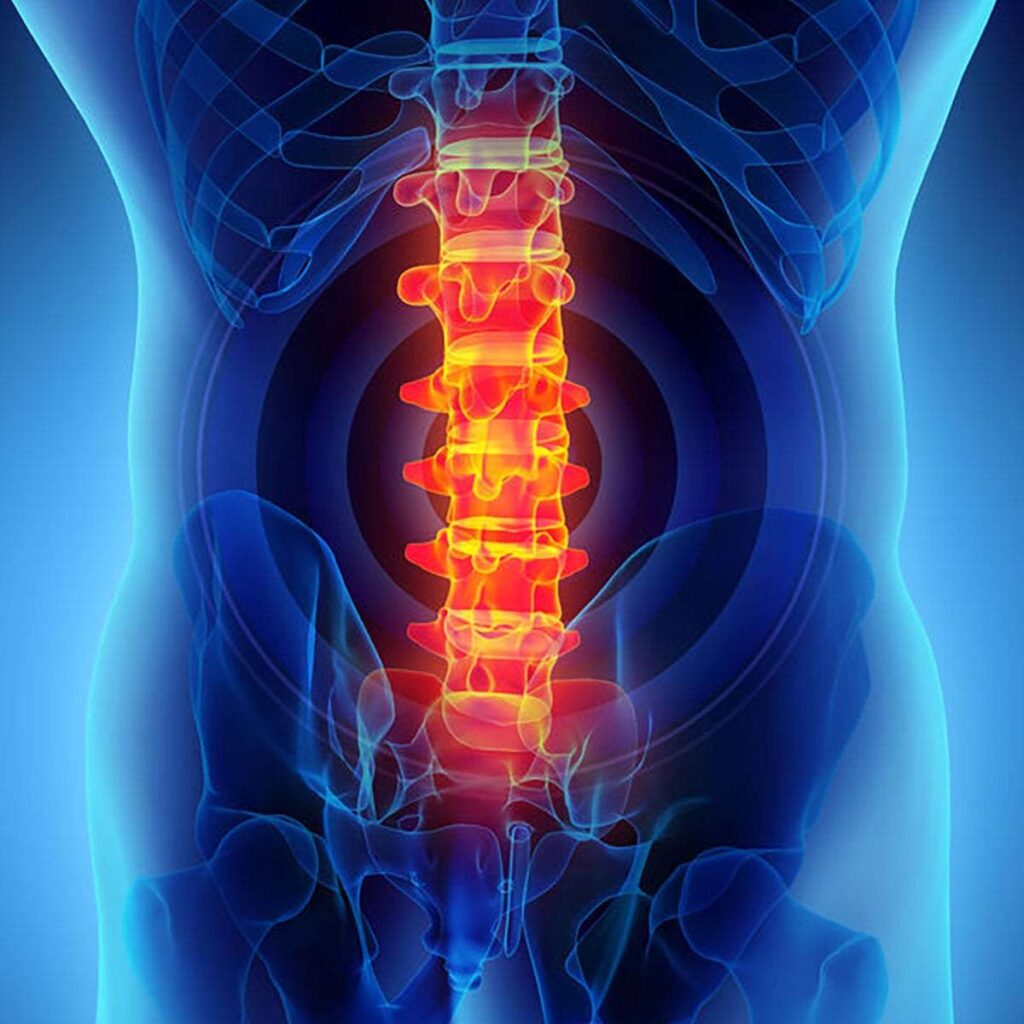
Types of Back Pain
Understanding the types of back pain is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Back pain is generally classified into the following categories:
Acute Back Pain
Acute back pain typically lasts a few days to a few weeks and is often caused by sudden injuries or improper movements.
Chronic Back Pain
Chronic back pain persists for 12 weeks or longer, even after the initial injury or underlying cause has been treated. This type often requires comprehensive management strategies.
Mechanical Back Pain
This type originates in the spine, intervertebral discs, or surrounding muscles and is usually aggravated by specific movements.
Radicular Back Pain
Radicular pain occurs when a spinal nerve is compressed or inflamed, often presenting as sciatica.
Common Causes of Back Pain
Back pain arises from a variety of causes, including lifestyle factors, injuries, and medical conditions. Key contributors include:
Poor Posture
Prolonged sitting, slouching, or improper ergonomics can strain the spine and lead to pain.
Muscle or Ligament Strain
Lifting heavy objects improperly or sudden awkward movements can cause strains, leading to discomfort.
Herniated or Bulging Discs
When spinal discs press on nearby nerves, they can cause pain, numbness, or weakness.
Degenerative Disc Disease
As people age, spinal discs lose hydration and elasticity, leading to chronic back pain.
Medical Conditions
Arthritis, scoliosis, osteoporosis, and infections can also contribute to back pain.
Psychological Factors
Stress, anxiety, and depression can exacerbate or even trigger back pain.
Symptoms of Back Pain
The symptoms of back pain vary widely depending on the cause and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Dull, aching pain in the lower or upper back
- Sharp or stabbing pain during movement
- Radiating pain down the legs (sciatica)
- Muscle stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities
Diagnosing Back Pain
Effective diagnosis is essential for targeted treatment. Medical professionals may use the following methods:
- Physical Examination: Assessing posture, range of motion, and reflexes
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to identify structural abnormalities
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluating nerve function to diagnose radiculopathy
Treatment Options for Back Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote better posture.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or prescription drugs for severe cases.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Acupuncture: Stimulating specific points to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Ergonomic adjustments and weight management.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is generally considered for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed. Options include:
- Discectomy: Removing herniated disc material pressing on nerves
- Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine
- Laminectomy: Removing part of the vertebra to relieve nerve pressure
Prevention Strategies
Preventing back pain involves adopting a proactive approach to spinal health:
- Exercise Regularly: Focus on strength training, stretching, and cardiovascular fitness.
- Maintain Good Posture: Use ergonomic furniture and practice proper sitting and standing habits.
- Lift Properly: Use your legs instead of your back when lifting heavy objects.
- Stay Active: Avoid prolonged sitting or inactivity.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent or worsening pain despite home remedies
- Pain following a traumatic injury
- Neurological symptoms like numbness or weakness
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel functions
A multifaceted condition requiring a tailored approach for effective management. By understanding the types, causes, and treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate pain and enhance their quality of life. Regular exercise, good posture, and timely medical intervention can make a significant difference in maintaining spinal health.