What is Eustachian Tube Congestion?
Eustachian tube congestion occurs when the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, become blocked or inflamed. These narrow passages regulate air pressure in the ear and drain excess fluid. When congested, they can cause discomfort, hearing difficulties, and even infections.
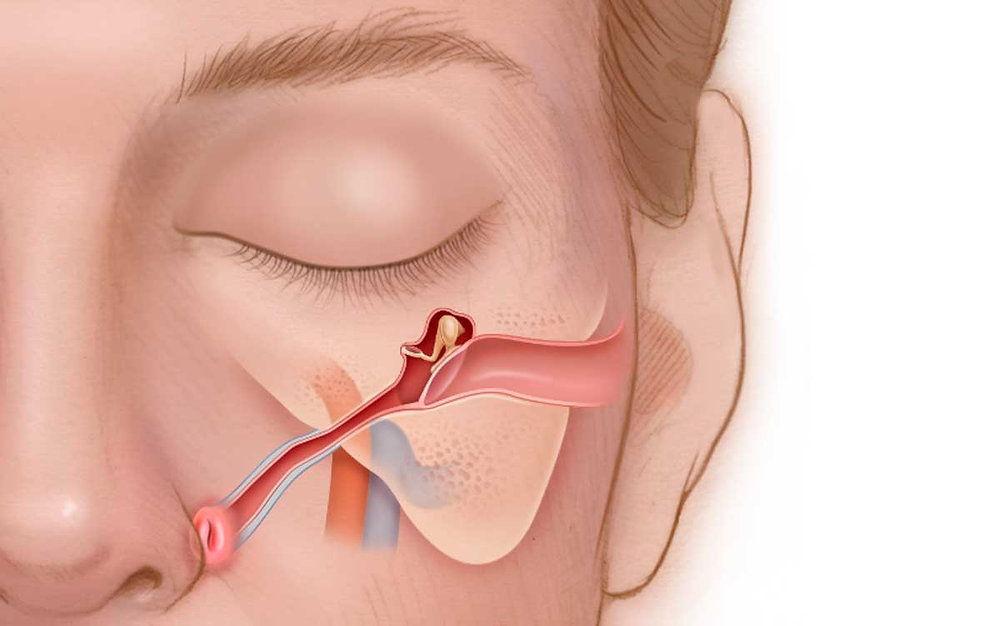
Common Causes of Eustachian Tube Congestion
Understanding the causes of Eustachian tube congestion is crucial for effective treatment. Common causes include:
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Colds, flu, and sinus infections often lead to nasal congestion, affecting the Eustachian tubes.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions cause inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, leading to blockage.
- Sinusitis: Chronic sinus infections can result in persistent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Changes in Altitude: Air travel, scuba diving, and driving in mountainous regions can disrupt Eustachian tube function.
- Ear Infections: Middle ear infections can cause fluid buildup and inflammation.
- Excessive Earwax: A blockage in the ear canal can contribute to pressure imbalances.
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Congestion
Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe complications. Key symptoms include:
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears
- Muffled hearing or temporary hearing loss
- Popping or crackling sensations
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or balance issues
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
How to Diagnose Eustachian Tube Congestion
A healthcare provider may diagnose Eustachian tube congestion through:
- Physical Examination: Checking the ears, nose, and throat for signs of infection or blockage.
- Tympanometry: Measuring eardrum movement to detect fluid buildup.
- Audiometry Tests: Assessing hearing function.
Effective Treatments
1. Medical Treatments
- Decongestants: Nasal sprays or oral decongestants reduce swelling in nasal passages and the Eustachian tubes.
- Antihistamines: Beneficial for allergy-induced congestion.
- Steroid Nasal Sprays: Reduce inflammation in persistent cases.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if an infection is present.
- Surgery: In severe cases, ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes) may be inserted to aid drainage.
2. Home Remedies and Natural Solutions
- Yawning, Swallowing, and Chewing Gum: Helps open the Eustachian tubes.
- Valsalva Maneuver: Pinch the nose, close the mouth, and gently blow to equalize pressure.
- Steam Inhalation: Clears nasal passages and relieves congestion.
- Saline Nasal Spray: Moistens nasal passages and clears blockages.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus secretions.
- Applying a Warm Compress: Helps soothe ear discomfort and improve drainage.
Complications of Untreated Eustachian Tube Congestion
If left untreated, prolonged Eustachian tube congestion may lead to:
- Chronic ear infections
- Middle ear fluid buildup (otitis media with effusion)
- Temporary or permanent hearing loss
- Balance problems
Prevention Tips
- Treat colds and allergies promptly.
- Use nasal sprays before flights or altitude changes.
- Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke and pollutants.
- Maintain good ear hygiene to prevent earwax buildup.