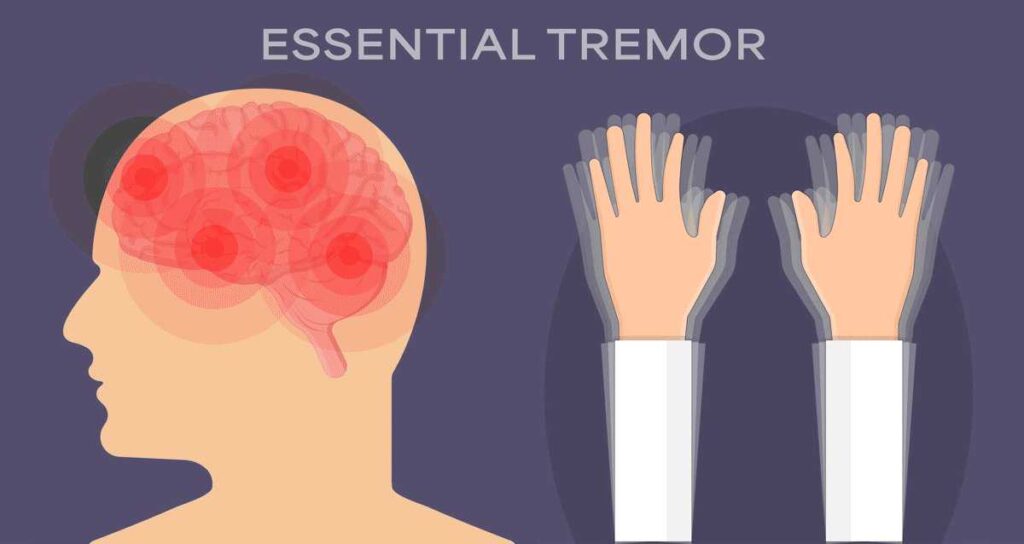
What Is Essential Tremor?
Essential tremor (ET) is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary and rhythmic shaking, most commonly affecting the hands but potentially involving the head, voice, and legs. Unlike Parkinson’s disease, ET is not associated with other neurodegenerative symptoms and tends to worsen with movement rather than at rest.
Causes of Essential Tremor
The exact cause of essential tremor remains unclear, but research suggests a genetic component, as approximately 50% of cases are hereditary. The condition is linked to abnormal activity in the thalamus, a brain region responsible for motor control. While ET can develop at any age, it is more prevalent in individuals over 40.
Symptoms of Essential Tremor
- Hand Tremors: Shaking that worsens with movement, affecting daily tasks such as writing or eating.
- Head and Voice Tremors: In some cases, tremors extend to the head, causing a nodding motion, or the voice, leading to a quivering speech.
- Worsening Over Time: Although gradual, the tremors often become more pronounced with age.
- Exacerbating Factors: Stress, fatigue, caffeine, and certain medications can intensify symptoms.
Diagnosing Essential Tremor
There is no single test for ET; diagnosis is based on medical history, clinical examination, and exclusion of other conditions. Physicians assess:
- Symptom Patterns: Tremor characteristics and affected body parts.
- Neurological Examination: Evaluating reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination.
- Performance Tests: Simple tasks like holding a glass of water or drawing spirals help assess tremor severity.
- Imaging Tests: While not always necessary, MRI or CT scans may rule out structural brain disorders.
Treatment Options
Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Depending on severity, management strategies include:
Medications
- Beta-Blockers (Propranolol): Commonly prescribed to reduce tremor amplitude.
- Anticonvulsants (Primidone): Effective in controlling symptoms, especially in patients unresponsive to beta-blockers.
- Benzodiazepines (Clonazepam, Alprazolam): Used in some cases but carry risks of dependence.
Physical Therapy
- Strength and Coordination Exercises: Improve motor control and minimize tremor impact.
- Assistive Devices: Weighted utensils and adaptive tools enhance daily functionality.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Reducing Caffeine and Alcohol: Helps manage tremor severity.
- Stress Management: Relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can alleviate symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Implanting electrodes in the thalamus to regulate tremor activity.
- Focused Ultrasound Therapy: A non-invasive approach using ultrasound waves to target brain areas responsible for tremors.
Essential Tremor vs. Parkinson’s Disease
While both conditions cause tremors, they differ in key aspects:
Outlook and Prognosis
Essential tremor is a progressive disorder, but it does not significantly reduce lifespan. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most individuals can manage symptoms effectively and maintain an active lifestyle.