What Is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It is a common condition affecting millions of men worldwide, often leading to stress, relationship issues, and a decrease in self-confidence.
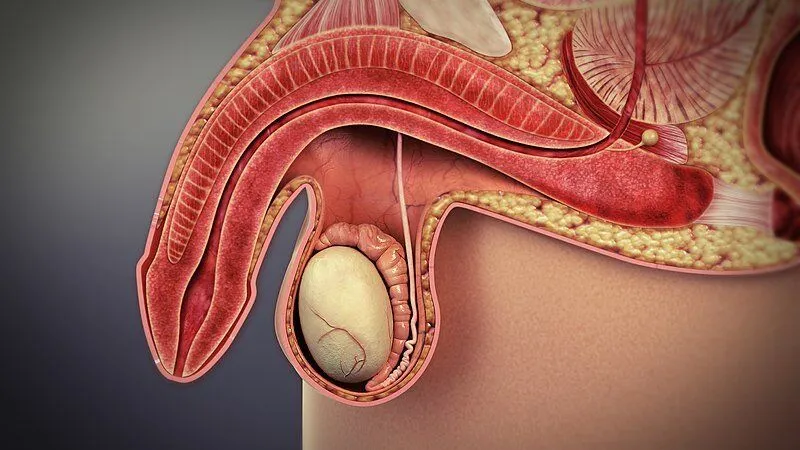
Common Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
ED can result from various physiological and psychological factors. Understanding these causes is essential for effective treatment.
1. Physical Causes
- Cardiovascular Diseases – Conditions like high blood pressure and atherosclerosis reduce blood flow to the penis.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels damage nerves and blood vessels, impairing erectile function.
- Obesity – Excess weight contributes to hormonal imbalances and reduced blood circulation.
- Hormonal Imbalances – Low testosterone levels can affect libido and erectile strength.
- Neurological Disorders – Conditions like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis disrupt nerve signals to the penis.
- Medications – Certain drugs, including antidepressants and blood pressure medications, may cause ED as a side effect.
- Substance Abuse – Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use impair blood flow and nerve function.
2. Psychological Causes
- Stress and Anxiety – Work pressure and personal issues can impact sexual performance.
- Depression – Low mood and lack of motivation contribute to ED.
- Performance Anxiety – Fear of failure can lead to a cycle of continued erectile difficulties.
- Relationship Issues – Poor communication and unresolved conflicts with a partner may result in sexual dysfunction.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
- Difficulty achieving an erection
- Trouble maintaining an erection during sexual activity
- Reduced sexual desire or libido
- Premature or delayed ejaculation
- Psychological distress related to sexual performance
Diagnosing Erectile Dysfunction
A comprehensive diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History Review – Discussing existing health conditions and lifestyle factors.
- Physical Examination – Checking for signs of underlying health issues.
- Blood Tests – Measuring hormone levels, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
- Ultrasound – Assessing blood flow in penile arteries.
- Psychological Evaluation – Identifying mental health factors contributing to ED.
Effective Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular Exercise – Improves cardiovascular health and increases blood flow.
- Healthy Diet – Eating nutrient-rich foods supports sexual function.
- Weight Management – Reduces the risk of obesity-related ED.
- Limiting Alcohol & Smoking – Enhances circulation and nerve function.
- Stress Reduction – Meditation, yoga, and therapy can improve mental well-being.
2. Medications for ED
- Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors – Includes sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra), which enhance blood flow.
- Hormone Therapy – Testosterone replacement therapy for men with low levels.
- Alprostadil Injections – Directly stimulates an erection by dilating blood vessels.
3. Natural Remedies for Erectile Dysfunction
- L-Arginine – Amino acid that boosts nitric oxide levels, improving blood flow.
- Ginseng – Traditional herb known to enhance sexual performance.
- Yohimbine – Derived from tree bark, may improve erectile function.
- Acupuncture – Some studies suggest it may alleviate ED symptoms.
4. Advanced Treatment Options
- Vacuum Erection Devices – Creates a vacuum around the penis to draw in blood.
- Penile Implants – Surgically inserted devices for severe ED cases.
- Shockwave Therapy – Uses sound waves to enhance penile blood circulation.
Preventing Erectile Dysfunction
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Monitor and manage chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
- Stay physically active and avoid prolonged sedentary habits.
- Prioritize mental health and manage stress effectively.
- Communicate openly with a partner about sexual health concerns.