The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis is crucial for regulating reproductive and hormonal function. Disruptions in this axis, especially in individuals with severe insulin resistance, can lead to infertility, irregular menstruation, hypogonadism, and metabolic disorders. Proper diagnosis is essential to tailor treatment strategies effectively.
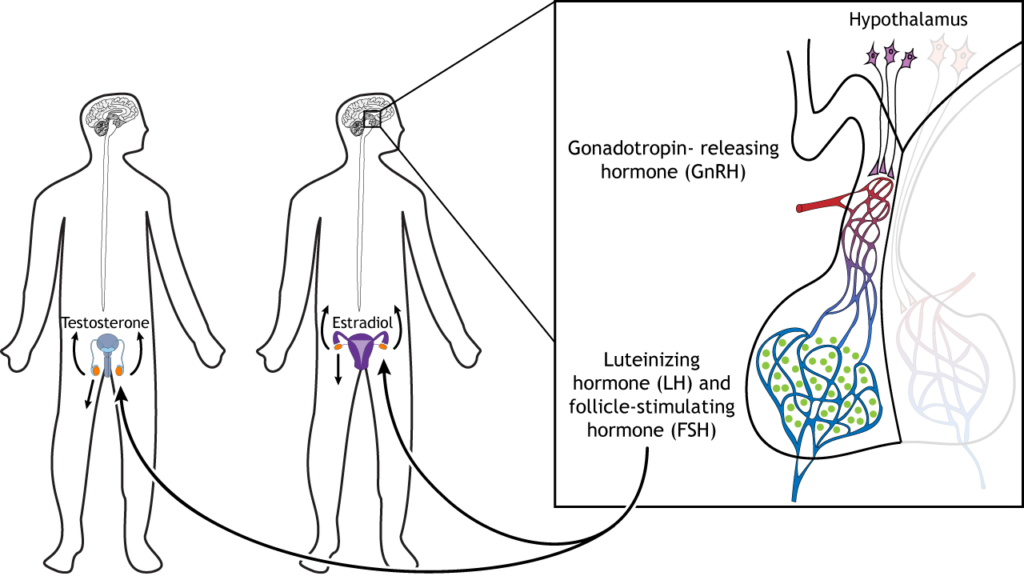
Understanding the HPG Axis
The HPG axis involves:
- Hypothalamus: Secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
- Pituitary Gland: Produces luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Gonads (Ovaries/Testes): Generate estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
When insulin resistance is present, hyperinsulinemia disrupts normal endocrine signaling, impacting GnRH secretion, LH/FSH balance, and gonadal function.
Diagnostic Approach to HPG Axis Dysfunction
1. Clinical Assessment
A thorough history and physical examination should include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles or amenorrhea in women
- Low libido, erectile dysfunction, or gynecomastia in men
- Signs of hyperandrogenism (e.g., hirsutism, acne)
- Body composition changes (central obesity, metabolic syndrome features)
2. Laboratory Investigations
Baseline Hormonal Panel
- Gonadotropins (LH, FSH): Assess pituitary response.
- Sex Steroid Levels:
- Testosterone (Total and Free) – Important in men and women with insulin resistance.
- Estradiol – Evaluates ovarian function.
- Progesterone – Checks luteal phase sufficiency.
- Prolactin: Elevated levels may indicate pituitary dysfunction.
- Thyroid Function Tests (TSH, Free T4): To rule out secondary causes.
- Cortisol (AM/PM Levels, Dexamethasone Suppression Test): Identifies adrenal hyperactivity affecting gonadal function.
Dynamic Endocrine Testing
- GnRH Stimulation Test: Differentiates hypothalamic vs. pituitary dysfunction.
- Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT): Assesses GH and ACTH response (contraindicated in cardiac disease).
- Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test: Evaluates hypothalamic-pituitary feedback in women.
3. Imaging Studies
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Brain: Detects hypothalamic or pituitary lesions.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: Assesses ovarian structure (e.g., polycystic ovaries in PCOS).
- Adrenal CT/MRI: Checks for hyperplasia or tumors affecting HPG axis.
4. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Panel
Since severe insulin resistance plays a central role, additional metabolic tests are required:
- Fasting Insulin and Glucose: Assesses hyperinsulinemia severity.
- HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance).
- Lipid Profile: Evaluates metabolic syndrome components.
- HbA1c: Monitors long-term glucose control.
Pathophysiology of Insulin Resistance in HPG Axis Dysfunction
Hyperinsulinemia increases androgen production via ovarian theca cells and adrenal glands, suppressing SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin) and leading to higher free testosterone levels, further disrupting gonadotropin regulation.
Differential Diagnostic test for hypothalamic pituitary gonadal axis
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
- Kallmann Syndrome (If anosmia is present)
- Primary Gonadal Failure
- Cushing’s Syndrome
- Prolactinoma