Acute Staph aureus sinusitis is a bacterial infection of the sinuses caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacterium. This condition can lead to severe discomfort, complications, and prolonged recovery if not treated promptly. In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for acute Staph. aureus sinusitis, providing a detailed guide to help you understand and manage this condition effectively.
Understanding Acute Staph Aureus Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis refers to the inflammation of the sinuses, typically lasting less than four weeks. When caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a common bacterium found on the skin and in the nasal passages, the infection can become particularly aggressive. Staph. aureus is known for its ability to develop resistance to antibiotics, making timely and accurate treatment essential.
Causes and Risk Factors
Staph. aureus sinusitis often occurs when the bacterium infiltrates the sinus cavities, usually following a viral upper respiratory infection or due to nasal trauma. Risk factors include:
- Weakened immune systems
- Chronic sinusitis
- Nasal polyps or structural abnormalities
- Frequent use of nasal decongestants
- Exposure to contaminated environments
Symptoms of Acute Staph. Aureus Sinusitis
The symptoms of acute Staph. aureus sinusitis are similar to those of other forms of sinusitis but may be more severe. Key symptoms include:
- Facial pain and pressure, particularly around the cheeks, forehead, and eyes
- Nasal congestion and discharge, often thick and yellow or green
- Fever and fatigue
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Cough caused by postnasal drip
In severe cases, patients may experience complications such as orbital cellulitis, meningitis, or abscess formation, necessitating immediate medical attention.
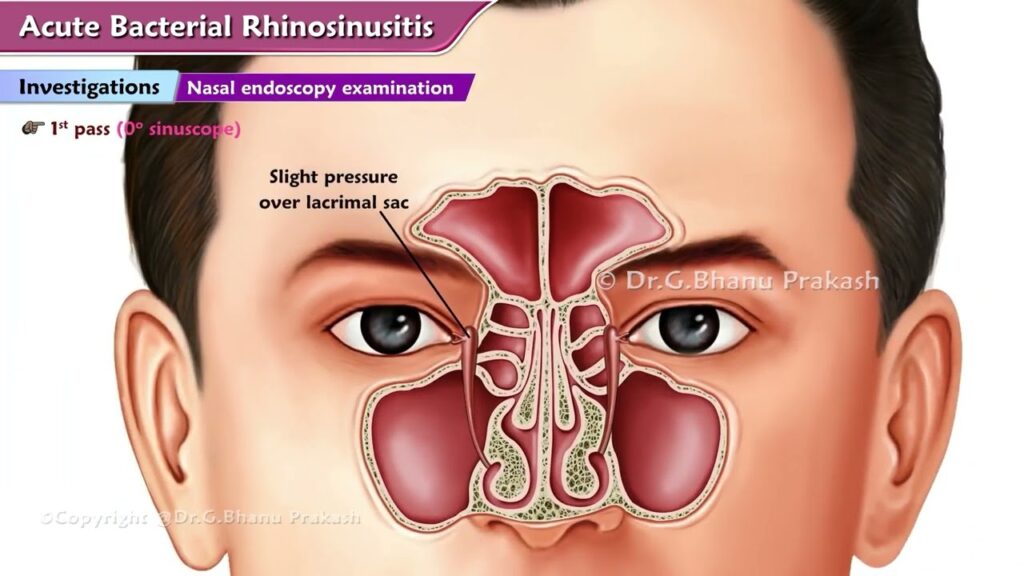
Diagnosing Acute Staph. Aureus Sinusitis
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment. Diagnostic methods include:
1. Clinical Evaluation
A thorough medical history and physical examination are the first steps. Physicians look for signs of sinus tenderness, nasal obstruction, and discolored nasal discharge.
2. Imaging Studies
CT scans or MRIs may be used to visualize the sinuses and identify blockages, inflammation, or complications.
3. Microbiological Testing
Nasal swabs or sinus aspirates are collected to identify the causative organism. Culture and sensitivity testing help determine the appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Treatment Options for Acute Staph. Aureus Sinusitis
1. Antibiotic Therapy
The cornerstone of treatment is antibiotics. For methicillin-sensitive Staph. aureus (MSSA), options include:
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate
- Cephalexin
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
For methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA), vancomycin or linezolid may be prescribed.
2. Symptomatic Relief
- Nasal corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Saline nasal irrigation to clear mucus
- Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
3. Surgical Intervention
In cases of chronic or complicated sinusitis, endoscopic sinus surgery may be required to remove blockages and improve drainage.
Preventing Acute Staph. Aureus Sinusitis
Preventive measures include:
- Practicing good hand hygiene
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections
- Using a humidifier to keep nasal passages moist
- Managing allergies and avoiding nasal irritants
Acute Staph. aureus sinusitis is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, patients can take proactive steps to manage their health effectively. If you suspect you have acute sinusitis, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.