Demodex blepharitis is a prevalent yet often underdiagnosed condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelid margins due to an overabundance of Demodex mites. These microscopic parasites inhabit human hair follicles and sebaceous glands, particularly around the eyes, leading to various ocular surface issues.
Demodex Mites: An Overview
Two species primarily affect humans:
- Demodex folliculorum: Resides in hair follicles, especially at the base of eyelashes.
- Demodex brevis: Inhabits sebaceous glands connected to hair follicles.
While typically harmless, an overpopulation can disrupt normal eyelid function and contribute to blepharitis.
Pathogenesis of Demodex Blepharitis
Demodex mites contribute to blepharitis through several mechanisms:
- Mechanical Damage: Mites consume epithelial cells at hair follicles, causing microabrasions and follicular distension.
- Bacterial Vector: They carry bacteria such as Staphylococcus epidermidis, potentially leading to inflammation.
- Inflammatory Response: Mite debris can trigger immune responses, resulting in eyelid inflammation.
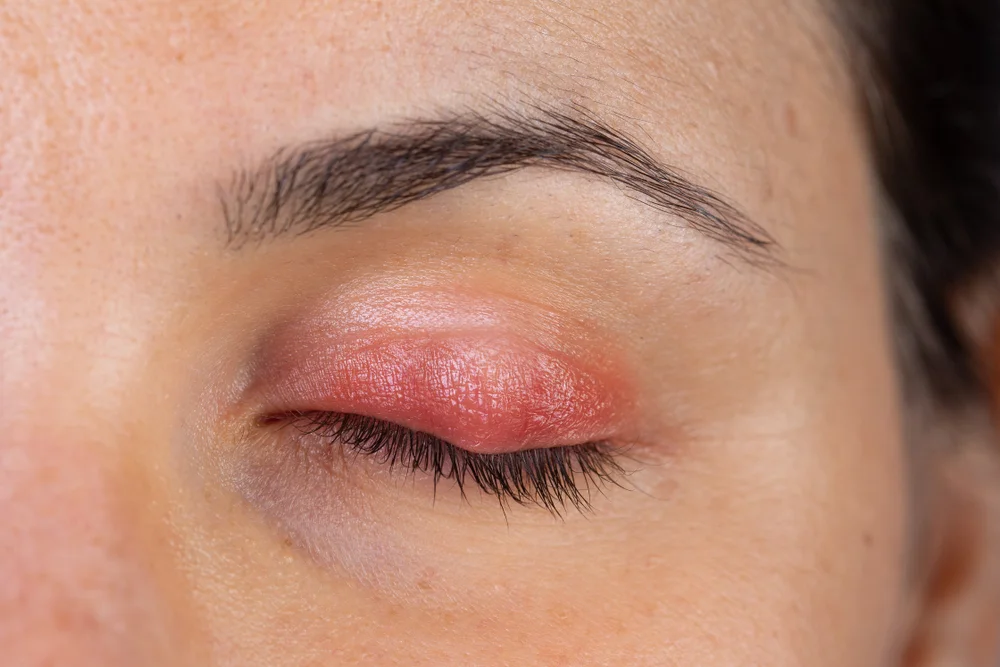
Clinical Manifestations
Patients may present with:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelid margins
- Itching or burning sensations
- Foreign body sensation
- Crusting or scaling at the base of eyelashes
- Misdirected or missing eyelashes
A distinctive feature is the presence of cylindrical dandruff (collarettes) at the base of the eyelashes.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosis involves:
- Clinical Examination: Identifying collarettes during slit-lamp examination.
- Microscopic Analysis: Evaluating epilated eyelashes for mites.
Management Strategies
Effective management includes:
- Eyelid Hygiene: Regular cleansing with non-irritating solutions to remove debris and reduce mite populations.
- Topical Treatments: Application of tea tree oil-based products has shown efficacy against Demodex mites.
- Prescription Medications: The FDA-approved lotilaner ophthalmic solution 0.25% (XDEMVY) targets Demodex mites specifically.
Preventive Measures
To prevent recurrence:
- Maintain diligent eyelid hygiene.
- Regularly clean bedding and towels.
- Avoid sharing personal items like makeup.
MYHEALTHMAG