Acute shoulder pain due to tendonitis is a common musculoskeletal condition that affects individuals of all ages. It results from inflammation or irritation of the tendons in the shoulder, often due to overuse, repetitive strain, or sudden injury. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for effective management and long-term relief.
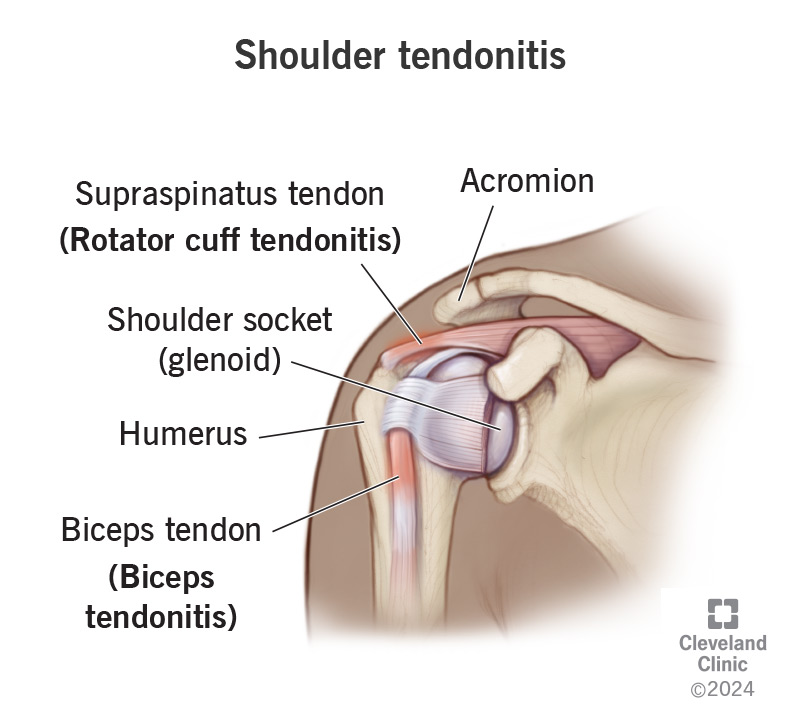
Causes of Shoulder Tendonitis
Tendonitis in the shoulder can develop due to various factors, including:
- Overuse and repetitive motion: Common in athletes and individuals with jobs requiring repetitive arm movements.
- Aging and wear-and-tear: Degenerative changes weaken the tendons over time.
- Poor posture: Leads to excessive strain on shoulder tendons.
- Trauma or sudden injury: Direct impact or sudden stretching of the tendon can trigger inflammation.
- Impingement syndrome: When the tendons are compressed between the bones of the shoulder, inflammation and pain occur.
Symptoms of Acute Shoulder Tendonitis
Patients with acute tendonitis experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Sharp or aching pain in the shoulder, especially with movement.
- Pain that worsens at night, particularly when lying on the affected shoulder.
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness.
- Weakness in the affected arm due to tendon inflammation.
- Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder joint.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Tendonitis
Clinical Examination
A healthcare provider assesses symptoms and conducts physical tests to evaluate pain, tenderness, and mobility.
Imaging Studies
- X-rays: Rule out fractures or arthritis.
- Ultrasound: Identifies inflammation and tendon tears.
- MRI scans: Provide detailed images of soft tissue damage.
Treatment Options for Acute Shoulder Tendonitis
Conservative Treatments
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding repetitive movements allows healing.
- Cold therapy: Reduces swelling and numbs pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises improve mobility.
- Corticosteroid injections: Provide temporary pain relief in severe cases.
Advanced Treatment Options
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Promotes tissue healing through growth factors.
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT): Stimulates tendon repair through acoustic waves.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Arthroscopic tendon debridement or repair in refractory cases.
Preventing Shoulder Tendonitis
- Proper warm-up and stretching before physical activities.
- Ergonomic adjustments in workspaces to maintain good posture.
- Strengthening exercises for the rotator cuff and shoulder muscles.
- Avoiding repetitive overhead movements to reduce strain on tendons.
Prognosis and Recovery
With early intervention and appropriate management, most cases of shoulder tendonitis resolve within a few weeks to months. Chronic cases may require prolonged therapy or surgical intervention for full recovery.
Acute shoulder pain due to tendonitis is a manageable condition with timely intervention. Proper diagnosis, effective treatment strategies, and preventive measures can help restore shoulder function and improve quality of life. Seeking medical guidance at the onset of symptoms ensures the best possible outcome.