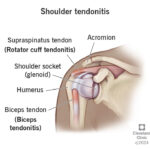
Acute shoulder pain due to bursitis is a common musculoskeletal condition that affects daily activities and overall quality of life. Bursitis occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles around the shoulder joint, become inflamed. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help individuals manage pain effectively and prevent chronic complications.
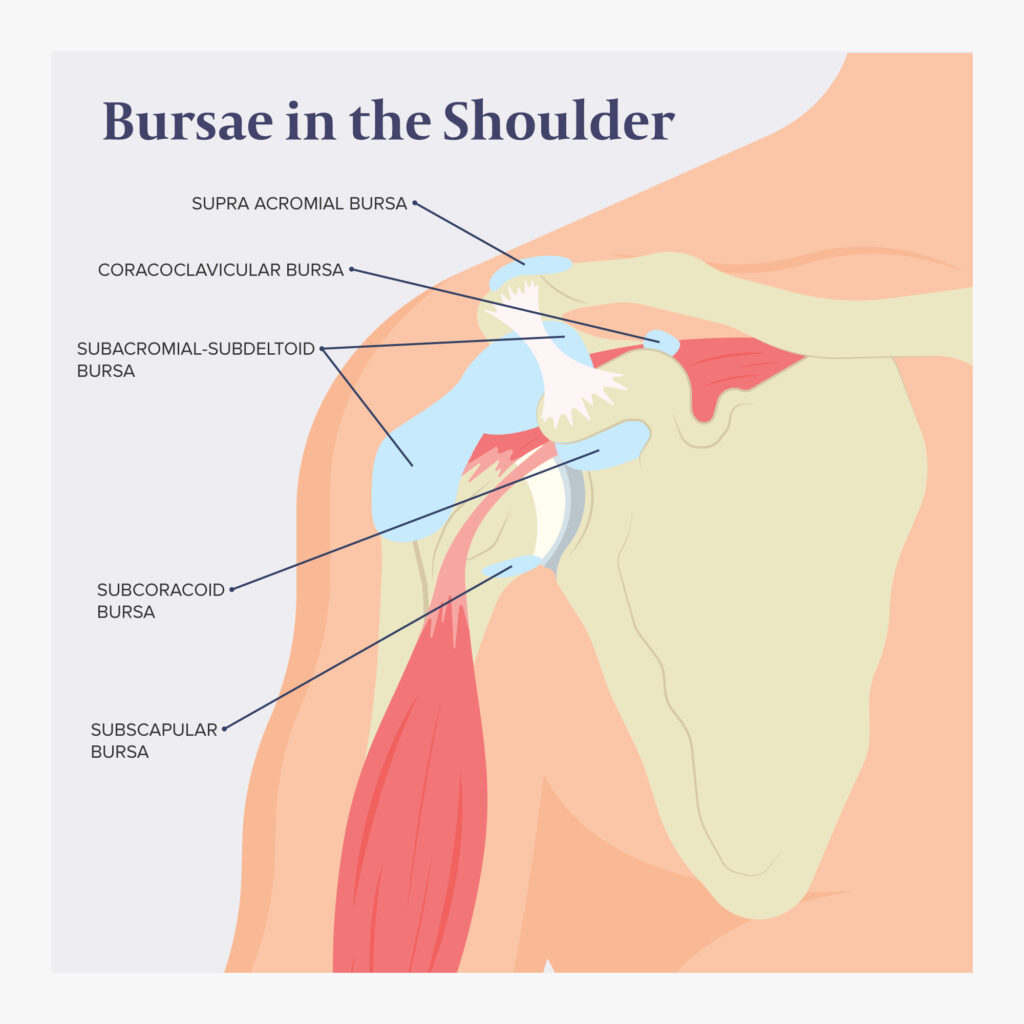
Causes of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis can develop due to various factors, including:
- Repetitive Motion Injuries: Overuse from activities like swimming, painting, or lifting heavy objects.
- Trauma or Injury: A direct impact to the shoulder can cause inflammation of the bursae.
- Age-related Wear and Tear: Degeneration of shoulder structures over time.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and gout increase the risk.
- Poor Posture: Incorrect shoulder mechanics place excessive strain on the bursae.
Symptoms of Acute Shoulder Bursitis
Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or aching pain in the shoulder, especially when moving the arm.
- Swelling and tenderness over the affected area.
- Limited range of motion, making it difficult to raise the arm.
- Pain at night, particularly when lying on the affected shoulder.
- Warmth and redness, indicating inflammation.
Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis involves:
- Physical Examination: Evaluating pain levels, swelling, and mobility restrictions.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Rule out fractures or arthritis.
- Ultrasound: Detects bursitis-related swelling.
- MRI: Provides a detailed view of soft tissue structures.
- Aspiration and Lab Tests: In cases of suspected infection, fluid may be extracted for analysis.
Treatment Options
1. Conservative Management
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid movements that aggravate pain.
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs reduces swelling and discomfort.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises improve shoulder function.
2. Medical Interventions
- Corticosteroid Injections: Provide significant pain relief by reducing inflammation.
- Aspiration: Draining excess fluid if swelling is severe.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Promotes healing in chronic cases.
3. Surgical Options
Arthroscopic Debridement: Minimally invasive procedure to remove damaged tissue.
Bursectomy: Removal of the inflamed bursa in severe cases.
Prevention Strategies
- Maintain Proper Shoulder Mechanics: Avoid excessive overhead movements.
- Strengthen Shoulder Muscles: Regular exercise to stabilize the joint.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Optimize workstation setup to reduce strain.
- Adequate Warm-up Before Activities: Prepares muscles and joints for movement.
- Timely Treatment of Minor Shoulder Issues: Prevents progression to bursitis.
Prognosis and Recovery
With early intervention and appropriate management, most cases of acute shoulder bursitis resolve within a few weeks. Chronic cases may require prolonged therapy or medical treatment. Ensuring proper rehabilitation and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce recurrence.
Acute shoulder pain due to bursitis is a treatable condition that requires a combination of rest, physiotherapy, and, in some cases, medical intervention. Identifying symptoms early and implementing preventive strategies can help maintain shoulder health and functionality.