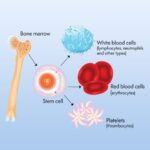
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (allo-BMT) is a critical therapeutic approach for various hematologic disorders. Despite advancements, challenges such as delays and failures persist, impacting patient outcomes. This article delves into the causes, preventive measures, and management strategies associated with these complications.
Causes of Delays in Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation
Several factors can contribute to delays in allo-BMT:
- Donor Availability: Identifying a suitable donor is paramount. HLA compatibility is crucial to minimize complications like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The search for an optimal match can be time-consuming, especially for patients with rare HLA types.
- Patient Condition: Pre-existing health issues or infections may necessitate postponing the transplant until the patient is stable enough to endure the procedure.
- Logistical Challenges: Coordinating between medical teams, securing necessary resources, and scheduling can introduce delays.
Causes of Failures in Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation
Failures in allo-BMT can manifest as graft rejection or relapse of the underlying disease. Key factors include:
- Graft Failure: This occurs when the transplanted marrow fails to engraft properly. Causes encompass immune-mediated mechanisms, infections, or inadequate stem cell numbers.
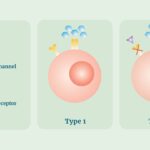
- Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD): A significant complication where donor immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. GVHD can be acute or chronic, affecting various organs and leading to transplant failure.
- Disease Relapse: The recurrence of the original disease post-transplant remains a primary cause of transplant failure.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To mitigate delays and failures in allo-BMT, the following strategies are essential:
- Enhanced Donor Matching: Utilizing advanced HLA typing techniques and expanding donor registries can improve match rates, reducing the risk of GVHD and graft failure.
- Pre-Transplant Conditioning: Optimizing conditioning regimens can enhance engraftment success and minimize complications.
- GVHD Prophylaxis and Treatment: Employing immunosuppressive therapies and monitoring for early signs of GVHD are crucial. Recent advancements include the use of mesenchymal stromal cells for treatment.
- Post-Transplant Monitoring: Regular assessments for chimerism, infections, and disease relapse enable timely interventions.