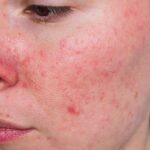
Acne rosacea keratitis is a serious ocular complication of rosacea that affects the eyes, leading to discomfort, vision problems, and potential corneal damage if untreated. This guide explores its symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options to help manage and mitigate its effects effectively.
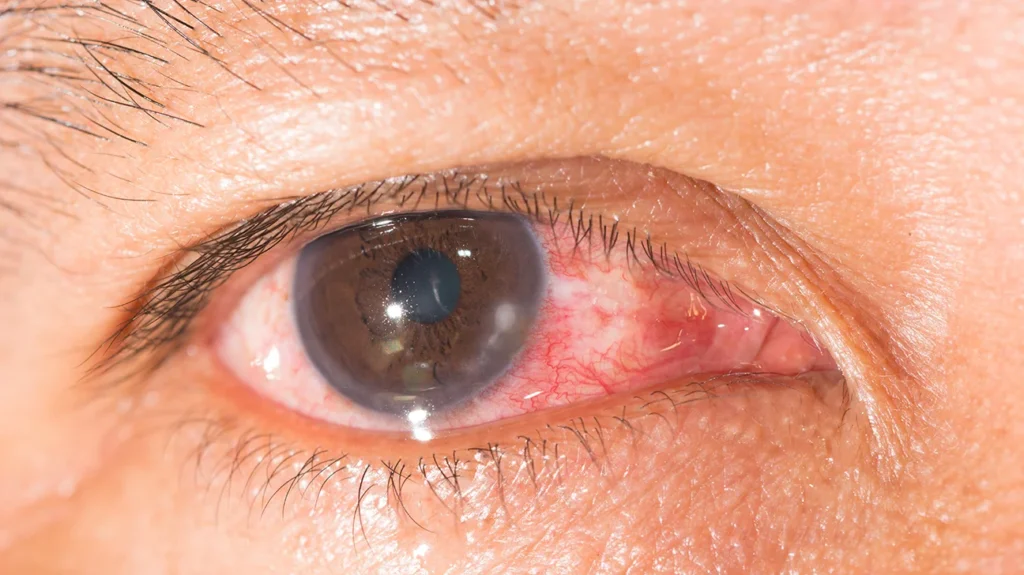
Understanding Acne Rosacea Keratitis
Acne rosacea keratitis, a subtype of ocular rosacea, involves inflammation of the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. This condition often develops in individuals with facial rosacea, particularly those with persistent redness and telangiectasia. It can result in chronic discomfort and visual disturbances if not promptly addressed.
Symptoms of Acne Rosacea Keratitis
Recognizing the symptoms of acne rosacea keratitis is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent eye redness.
- Gritty or foreign body sensation in the eyes.
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia).
- Blurred vision.
- Watery or dry eyes.
- Eyelid inflammation (blepharitis).
These symptoms may range from mild to severe, with severe cases potentially causing corneal ulceration and scarring, leading to vision loss.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of acne rosacea keratitis remains unclear, but it is closely associated with facial rosacea. Key contributing factors include:
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation in facial rosacea may extend to the ocular region, affecting the cornea and surrounding tissues.
- Abnormal Immune Response: An overactive immune response to environmental triggers or microbial antigens can exacerbate symptoms.
- Dysfunctional Meibomian Glands: Dysfunction in these oil-secreting glands within the eyelids may lead to dry eyes, increasing susceptibility to keratitis.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of rosacea increases the likelihood of developing its ocular manifestations.
Risk factors include prolonged sun exposure, certain medications, alcohol consumption, and stress, all of which can trigger or exacerbate rosacea.
Diagnosis of Acne Rosacea Keratitis
Diagnosis requires a thorough clinical evaluation by an ophthalmologist or dermatologist. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Patient History: A review of facial rosacea symptoms and triggers.
- Eye Examination: Slit-lamp examination to assess corneal inflammation and detect abnormalities in the tear film or eyelid margins.
- Corneal Staining: Use of fluorescein dye to identify areas of corneal damage or ulceration.
- Tear Film Analysis: Assessment of tear production and quality to evaluate dry eye syndrome.
Early diagnosis is critical to prevent long-term complications, such as vision loss or chronic ocular discomfort.
Treatment and Management of Acne Rosacea Keratitis
Pharmacologic Interventions
Treatment of acne rosacea keratitis typically involves a combination of topical and systemic therapies:
- Topical Antibiotics: Medications like erythromycin or metronidazole are applied to the eyelid margins to reduce bacterial overgrowth and inflammation.
- Oral Antibiotics: Tetracyclines (e.g., doxycycline) are commonly prescribed for their anti-inflammatory properties and effectiveness in controlling moderate to severe cases.
- Steroid Eye Drops: Short-term use of corticosteroid eye drops helps control severe inflammation, though prolonged use should be avoided due to the risk of complications like glaucoma.
- Artificial Tears: Lubricating eye drops alleviate dryness and improve tear film stability.
Mechanical Treatments
- Eyelid Hygiene: Regular cleaning of the eyelids with warm compresses and gentle scrubbing helps manage blepharitis and meibomian gland dysfunction.
- Meibomian Gland Expression: Performed by an ophthalmologist, this procedure helps unblock the meibomian glands, improving lipid production in the tear film.
Lifestyle Modifications
Patients should adopt lifestyle changes to minimize triggers, including:
- Avoiding spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine.
- Wearing sunglasses to protect against UV rays and environmental irritants.
- Using a humidifier to maintain optimal air moisture levels.
Potential Complications of Untreated Acne Rosacea Keratitis
Failure to treat acne rosacea keratitis can result in:
- Corneal Ulcers: Open sores on the cornea that can lead to scarring.
- Permanent Vision Loss: Advanced cases may cause irreversible damage to the cornea.
- Chronic Discomfort: Persistent symptoms that diminish quality of life.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With prompt and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for acne rosacea keratitis is favorable. Patients should adhere to prescribed treatments, attend regular follow-ups, and actively manage triggers to minimize recurrences. Collaboration between dermatologists and ophthalmologists ensures comprehensive care.