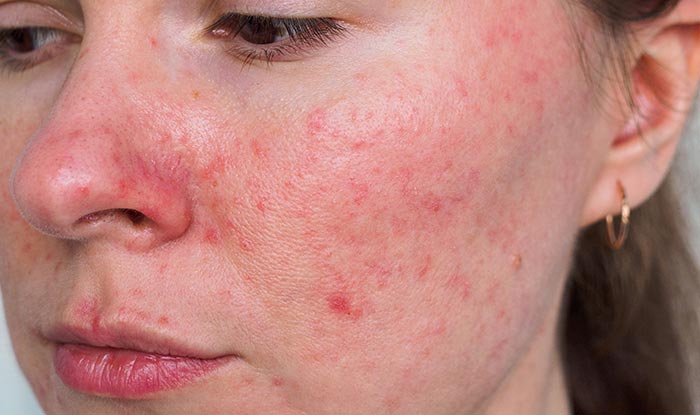
Acne rosacea, commonly referred to as rosacea, is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. Characterized by redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like pustules, it can significantly impact one’s confidence and quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing the condition effectively.
What is Acne Rosacea?
Acne rosacea is a dermatological condition that typically affects adults, with symptoms ranging from mild redness to severe inflammation and skin thickening. It often appears on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. While the exact cause remains unclear, genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and an overactive immune response play crucial roles.
Symptoms of Acne Rosacea
1. Facial Redness (Erythema)
Persistent redness is a hallmark of rosacea. It is caused by dilated blood vessels near the skin’s surface.
2. Visible Blood Vessels (Telangiectasia)
In some cases, small blood vessels become visible, especially on the cheeks and nose.
3. Acne-Like Pustules
While not the same as traditional acne, rosacea can cause red bumps and pus-filled lesions.
4. Thickened Skin
In severe cases, particularly in men, the skin can thicken, leading to a condition called rhinophyma, where the nose appears enlarged and bulbous.
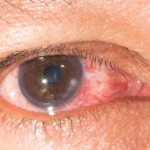
5. Eye Involvement (Ocular Rosacea)
Rosacea can affect the eyes, causing dryness, irritation, and swollen eyelids.
Causes and Triggers of Acne Rosacea
1. Genetic Factors
A family history of rosacea increases susceptibility to the condition.
2. Environmental Triggers
- Sunlight Exposure: UV rays can exacerbate rosacea symptoms.
- Temperature Extremes: Hot or cold weather may trigger flare-ups.
3. Dietary Triggers
- Spicy foods, hot drinks, and alcohol are common culprits.
4. Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress can intensify symptoms, highlighting the importance of stress management in treatment.
5. Skin Microbiome
The Demodex mite, a microorganism commonly found on human skin, may contribute to inflammation in rosacea.
Diagnosis of Acne Rosacea
Clinical Examination
A dermatologist typically diagnoses rosacea based on visible symptoms. There are no specific tests, but thorough medical and family history evaluations help rule out other conditions.
Subtype Classification
Rosacea is categorized into four subtypes:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea: Redness and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Acne-like breakouts.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Skin thickening, especially around the nose.
- Ocular Rosacea: Eye involvement.
Treatment Options for Acne Rosacea
1. Topical Medications
- Metronidazole: A commonly prescribed antibiotic gel that reduces inflammation.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps reduce redness and swelling.
- Ivermectin: Effective in reducing symptoms caused by the Demodex mite.
2. Oral Medications
- Tetracyclines: Oral antibiotics like doxycycline are prescribed for moderate to severe cases.
- Isotretinoin: For severe, treatment-resistant rosacea, isotretinoin may be considered.
3. Laser and Light Therapy
- Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL): Targets visible blood vessels to reduce redness.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Improves skin texture and minimizes flare-ups.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen daily.
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoid trigger foods and beverages.
- Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness and meditation can help reduce flare-ups.
Skin Care for Acne Rosacea
Gentle Cleansing
Use mild, non-comedogenic cleansers to avoid irritation.
Moisturizing
Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to maintain the skin barrier.
Makeup for Coverage
Green-tinted primers can help neutralize redness.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
While rosacea cannot be cured, consistent management strategies can keep symptoms under control:
- Avoid Known Triggers: Keep a diary to identify personal triggers.
- Follow a Dermatologist’s Plan: Regular consultations ensure treatments are effective.
- Protect Skin: Always use sun protection and avoid harsh skincare products.
Acne rosacea is a complex and chronic skin condition that requires a tailored approach for effective management. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and triggers, patients and healthcare providers can work together to create a comprehensive treatment plan. With the right combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve clearer, healthier skin and improved quality of life.