Acute Proteus mirabilis otitis externa is a severe bacterial infection affecting the external ear canal. This opportunistic pathogen can lead to significant inflammation, pain, and complications if untreated. Understanding its pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is essential for effective management.
Pathophysiology of Proteus mirabilis Infection
Proteus mirabilis is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacterium known for its motility and urease production. It colonizes the ear canal, disrupting the natural microbiota and leading to infection.
Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to susceptibility:
- Prolonged Moisture Exposure: Frequent swimming or humid environments.
- Trauma to Ear Canal: Excessive ear cleaning or foreign objects.
- Immunocompromised Conditions: Diabetes, cancer, or immunosuppressive therapy.
- Chronic Otitis Media History: Previous ear infections increase risk.
- Poor Ear Hygiene: Accumulation of debris fosters bacterial growth.
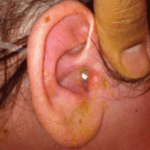
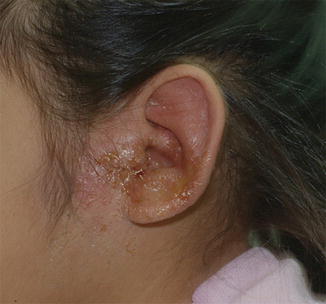
Symptoms
Patients typically experience:
- Severe Ear Pain: Often worsens with movement.
- Purulent Discharge: Thick, foul-smelling ear drainage.
- Swelling and Redness: Inflammation around the ear canal.
- Hearing Loss: Conductive hearing impairment due to obstruction.
- Fever and Malaise: Systemic symptoms in severe cases.
Diagnosis
1. Clinical Examination
- Otoscopic findings: Swollen, erythematous ear canal with discharge.
- Palpation: Tenderness around the auricle and tragus.
2. Microbiological Tests
- Culture and Sensitivity: Identifies Proteus mirabilis and determines antibiotic resistance.
- Gram Staining: Confirms bacterial presence.
3. Imaging Studies
- CT Scan or MRI: Required if infection spreads to deeper structures.
Treatment Strategies
1. Antibiotic Therapy
- Topical Antibiotics: Ciprofloxacin, neomycin-polymyxin B, or gentamicin.
- Oral or IV Antibiotics: Fluoroquinolones or third-generation cephalosporins in severe cases.
- Beta-lactamase Inhibitors: If resistance is suspected.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Pain Management
- NSAIDs: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief.
- Steroid Ear Drops: Reduce inflammation and swelling.
3. Ear Hygiene and Preventive Measures
- Gentle Cleaning: Avoid excessive cotton swab use.
- Keep Ears Dry: Use earplugs while swimming.
- Avoid Irritants: Prevent exposure to allergens and pollutants.
Complications
Untreated infections may lead to:
- Chronic Otitis Externa
- Malignant Otitis Externa (especially in diabetics)
- Hearing Impairment
- Deep Tissue Infections
Acute Proteus mirabilis otitis externa requires prompt medical intervention to prevent severe complications. Proper diagnosis, targeted antibiotic therapy, and preventive measures play a crucial role in managing and reducing recurrence rates.