The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the world in profound ways, prompting an urgent global effort to develop, distribute, and administer vaccines to combat the virus. As we continue to navigate the effects of the pandemic, COVID-19 vaccination remains one of the most crucial measures in mitigating its impact. This article provides a comprehensive overview of COVID-19 vaccination, including its types, benefits, side effects, and the global vaccination effort that is underway.
Understanding the Importance of COVID-19 Vaccination
COVID-19 vaccination is essential for controlling the spread of the virus, preventing severe illness, and reducing the risk of death. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight the virus, providing immunity without causing the disease itself. By vaccinating large populations, we can achieve herd immunity, which significantly reduces the spread of the virus within communities.
COVID-19 Vaccination and Public Health
Vaccination programs play a pivotal role in protecting not only individual health but also the broader community. Widespread immunization helps lower the overall number of cases, preventing healthcare systems from becoming overwhelmed. In addition, vaccines contribute to economic recovery by reducing healthcare costs and enabling safer social and economic activities.
Types of COVID-19 Vaccines
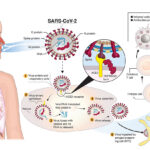
Several types of COVID-19 vaccines have been developed and approved for emergency use or full authorization by various health agencies worldwide. These vaccines can be broadly categorized into three groups: mRNA vaccines, viral vector vaccines, and protein subunit vaccines.
1. mRNA Vaccines
mRNA vaccines, such as the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, are groundbreaking in their use of messenger RNA to instruct cells in the body to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. This response prepares the body to fight the virus if it is encountered in the future. These vaccines have shown high efficacy in preventing severe disease and transmission.
2. Viral Vector Vaccines
The AstraZeneca-Oxford and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are examples of viral vector vaccines. These vaccines use a harmless virus (not the coronavirus) to deliver genetic material into cells. This material prompts the production of the spike protein found on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, prompting an immune response. These vaccines have been proven to be safe and effective, especially in preventing severe cases of COVID-19.
3. Protein Subunit Vaccines
Protein subunit vaccines, like Novavax, use harmless pieces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, such as its spike protein, to stimulate an immune response without using the live virus that causes COVID-19. This method has been widely used in vaccine development for other diseases and provides a reliable option for those who may not respond well to other vaccine types.
The Benefits of COVID-19 Vaccination
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination extend far beyond personal protection. Widespread vaccination is essential for achieving the following:
1. Reducing Severe Illness and Death
COVID-19 vaccines are highly effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Although breakthrough infections can occur, vaccinated individuals are far less likely to experience severe outcomes compared to those who are unvaccinated.
2. Preventing the Spread of COVID-19
Vaccines not only protect individuals but also help reduce the transmission of the virus within communities. As more people get vaccinated, the virus has fewer opportunities to spread, which is key to achieving herd immunity.
3. Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups, such as the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with underlying health conditions, are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes. Vaccination plays a critical role in safeguarding these vulnerable populations from the virus.
4. Promoting Economic Recovery
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused significant economic disruptions worldwide. By preventing illness and reducing healthcare burdens, vaccination contributes to the recovery of economies by allowing businesses to reopen, tourism to resume, and workers to return to their jobs with greater confidence.
Side Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines
Like all vaccines, COVID-19 vaccines can cause side effects. However, these side effects are generally mild and short-lived, with most individuals experiencing no serious reactions.
Common Side Effects
- Pain at the injection site
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Chills or fever
These side effects usually resolve within a few days and are a sign that the body is building immunity.
Rare Side Effects
In rare cases, more serious side effects such as allergic reactions or blood clotting disorders have been reported, particularly with the AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson vaccines. However, these side effects are extremely uncommon, and the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks for most people.
The Global COVID-19 Vaccination Effort
The global vaccination campaign is one of the largest public health initiatives in history. As of 2025, billions of COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered worldwide. While progress has been made, challenges remain, especially in low-income countries where access to vaccines is limited.
Vaccine Equity
Ensuring equitable access to vaccines is crucial for controlling the global pandemic. Efforts such as the COVAX initiative aim to provide vaccines to lower-income countries, ensuring that all nations have the resources to protect their populations from the virus.
Vaccine Rollout and Logistics
Vaccine distribution requires robust logistics, including the cold storage of certain vaccines, to ensure that doses remain effective. Global cooperation between governments, organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO), and pharmaceutical companies is vital to overcoming logistical hurdles and ensuring that vaccines reach every corner of the globe.
The Future of COVID-19 Vaccination
As new variants of the virus continue to emerge, ongoing research into vaccine development and booster doses is essential. Future vaccines may be adapted to better target variants or provide longer-lasting immunity.
mRNA Vaccine Advancements
Research into mRNA technology is expanding beyond COVID-19, with potential applications for other diseases such as cancer, HIV, and Zika virus. The success of mRNA vaccines in combating COVID-19 paves the way for exciting new medical advancements.