Corpus luteum insufficiency syndrome, also known as luteal phase defect (LPD), is a condition characterized by inadequate production of progesterone during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. This hormonal deficiency impairs the endometrium’s ability to support embryo implantation and maintain early pregnancy, often leading to infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
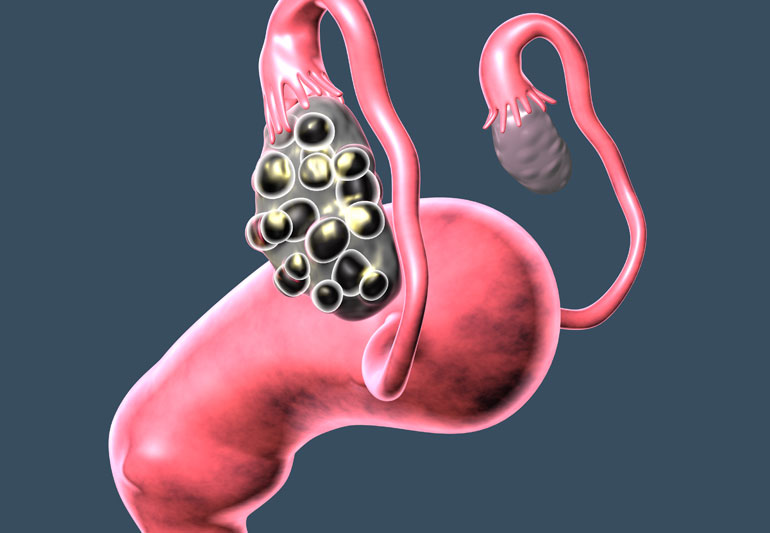
The Role of the Corpus Luteum in the Menstrual Cycle
The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure formed in the ovary after ovulation. Its primary function is to secrete progesterone, a hormone essential for preparing the uterine lining (endometrium) for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to a decrease in progesterone levels and the onset of menstruation.
Causes of Corpus Luteum Insufficiency
Several factors can contribute to corpus luteum insufficiency:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and hyperprolactinemia can disrupt the hormonal regulation necessary for proper corpus luteum function.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excessive physical exercise, significant stress, and extreme body weight (either underweight or overweight) can adversely affect progesterone production.
- Medical Conditions: Endometriosis and other reproductive system disorders may impair ovarian function, leading to insufficient progesterone secretion.
Symptoms Associated with Corpus Luteum Insufficiency
Individuals with corpus luteum insufficiency may experience:
- Menstrual Irregularities: Shortened menstrual cycles or spotting between periods.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving due to an inhospitable uterine environment for embryo implantation.
- Recurrent Miscarriages: Early pregnancy losses resulting from inadequate endometrial support.
Diagnosing Corpus Luteum Insufficiency
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Hormonal Assessments: Blood tests to measure mid-luteal phase progesterone levels.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Transvaginal ultrasounds to evaluate endometrial thickness and ovarian morphology.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Sampling of the uterine lining to assess its development and receptivity.
Treatment Options for Corpus Luteum Insufficiency
Management strategies may include:
- Progesterone Supplementation: Administering progesterone orally, vaginally, or via injections to support the luteal phase.
- Ovulation Induction: Medications such as clomiphene citrate or human menopausal gonadotropins (hMG) to stimulate follicular development and enhance corpus luteum function.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Addressing factors like stress, exercise, and body weight to optimize hormonal balance.
Corpus luteum insufficiency syndrome is a significant factor in reproductive challenges, particularly concerning infertility and early pregnancy loss. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for individuals affected by this condition. Consultation with a healthcare provider specializing in reproductive endocrinology is recommended for personalized evaluation and treatment.