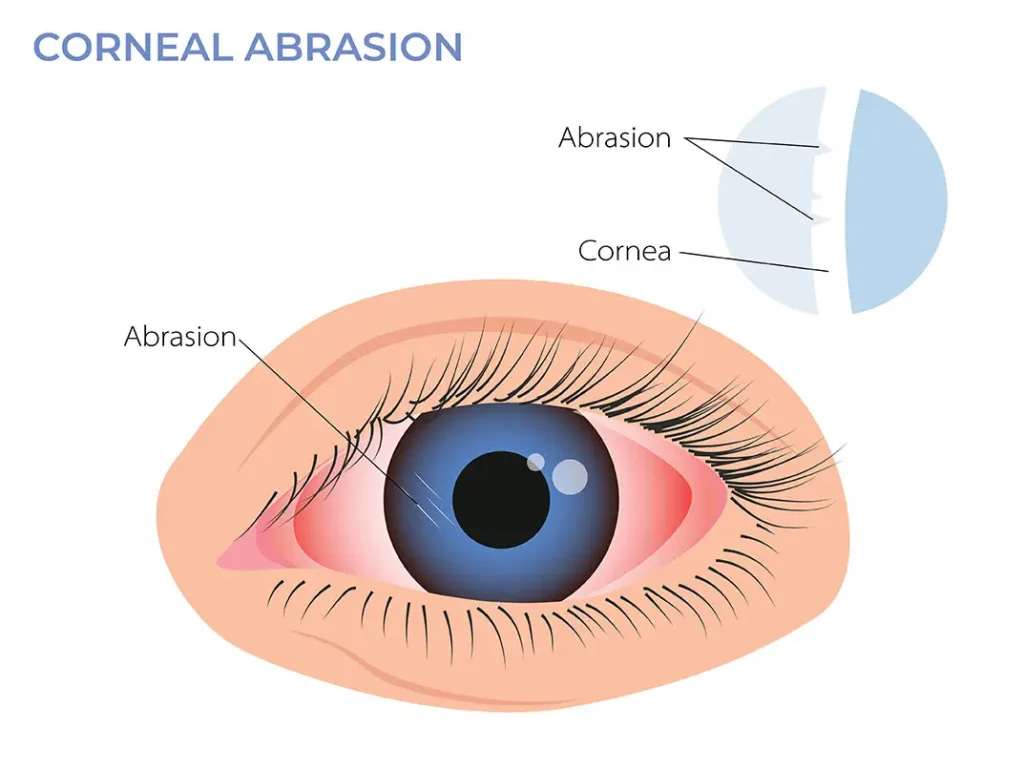
A corneal abrasion refers to a scratch or injury to the cornea—the transparent, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. This condition is prevalent and can lead to significant discomfort, visual disturbances, and an increased risk of infection if not promptly addressed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and preventive measures is essential for effective management and prevention of corneal abrasions.
Causes of Corneal Abrasion
Corneal abrasions typically result from direct trauma or foreign bodies contacting the eye’s surface. Common causes include:
- Foreign Objects: Particles such as dust, sand, metal shavings, or plant matter can enter the eye and scratch the cornea, especially if the eye is rubbed in an attempt to remove the irritant.
- Contact Lenses: Improper use of contact lenses, including wearing damaged lenses, extended wear beyond recommended durations, or poor hygiene practices, can lead to corneal abrasions.
- Trauma: Accidental pokes from fingers, makeup brushes, tree branches, or other objects can cause scratches on the corneal surface.
- Dry Eyes: Severe dryness can make the cornea more susceptible to abrasions, as the protective tear film is compromised.
Symptoms of Corneal Abrasion
Individuals with a corneal abrasion may experience the following symptoms:
- Eye Pain: Ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain, often described as a sharp or throbbing sensation.
- Redness: Inflammation of the eye due to irritation.
- Tearing: Excessive tear production as the eye attempts to flush out foreign particles.
- Photophobia: Sensitivity to light, causing discomfort in bright environments.
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty focusing due to the irregular corneal surface.
- Foreign Body Sensation: A persistent feeling that something is in the eye, even after removing any apparent irritants.
These symptoms typically manifest immediately after the injury and may vary in intensity based on the abrasion’s severity.
Diagnosis of Corneal Abrasion
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. An eye care professional will conduct a comprehensive eye examination, which may include:
- Visual Acuity Test: Assessing the clarity of vision to determine the impact of the abrasion.
- Fluorescein Staining: Applying a special dye to the eye’s surface, which highlights abrasions under blue light, allowing for precise identification of the affected area.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: Using a microscope with a bright light to provide a magnified view of the cornea and detect any irregularities or foreign bodies.
Treatment Options for Corneal Abrasion
Treatment aims to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent complications such as infections. Common approaches include:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops or Ointments: Prescribed to prevent bacterial infections during the healing process.
- Lubricating Eye Drops: Artificial tears help maintain moisture on the eye’s surface, providing comfort and facilitating healing.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications may be recommended to manage discomfort.
- Eye Patching: In certain cases, covering the affected eye with a patch can reduce discomfort from blinking and exposure, though this practice is less common today.
- Avoidance of Contact Lenses: Patients are advised to refrain from wearing contact lenses until the abrasion has fully healed to prevent further irritation or potential infection.
Most minor corneal abrasions heal within 24 to 48 hours. However, larger or more severe abrasions may require a longer healing period and close monitoring by an eye care professional.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing corneal abrasions involves adopting protective measures and practicing good eye hygiene:
- Protective Eyewear: Wearing safety glasses or goggles during activities that pose a risk of eye injury, such as woodworking, metalworking, or contact sports, can significantly reduce the risk.
- Proper Contact Lens Use: Adhering to recommended guidelines for contact lens wear, including proper cleaning, storage, and timely replacement, is essential.
- Avoid Rubbing Eyes: Refraining from rubbing the eyes, especially when a foreign body is present, can prevent potential abrasions.
- Regular Eye Examinations: Routine check-ups with an eye care professional can help identify and address issues that may increase the risk of corneal abrasions.