complicated peptostreptococcus peritonitis, the inflammation of the peritoneum, poses significant clinical challenges, especially when involving anaerobic bacteria such as Peptostreptococcus species. These gram-positive anaerobic cocci, part of the normal human microbiota, can become pathogenic under certain conditions, leading to severe intra-abdominal infections. This article delves into the complexities of Peptostreptococcus peritonitis, encompassing its pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methodologies, and treatment protocols.
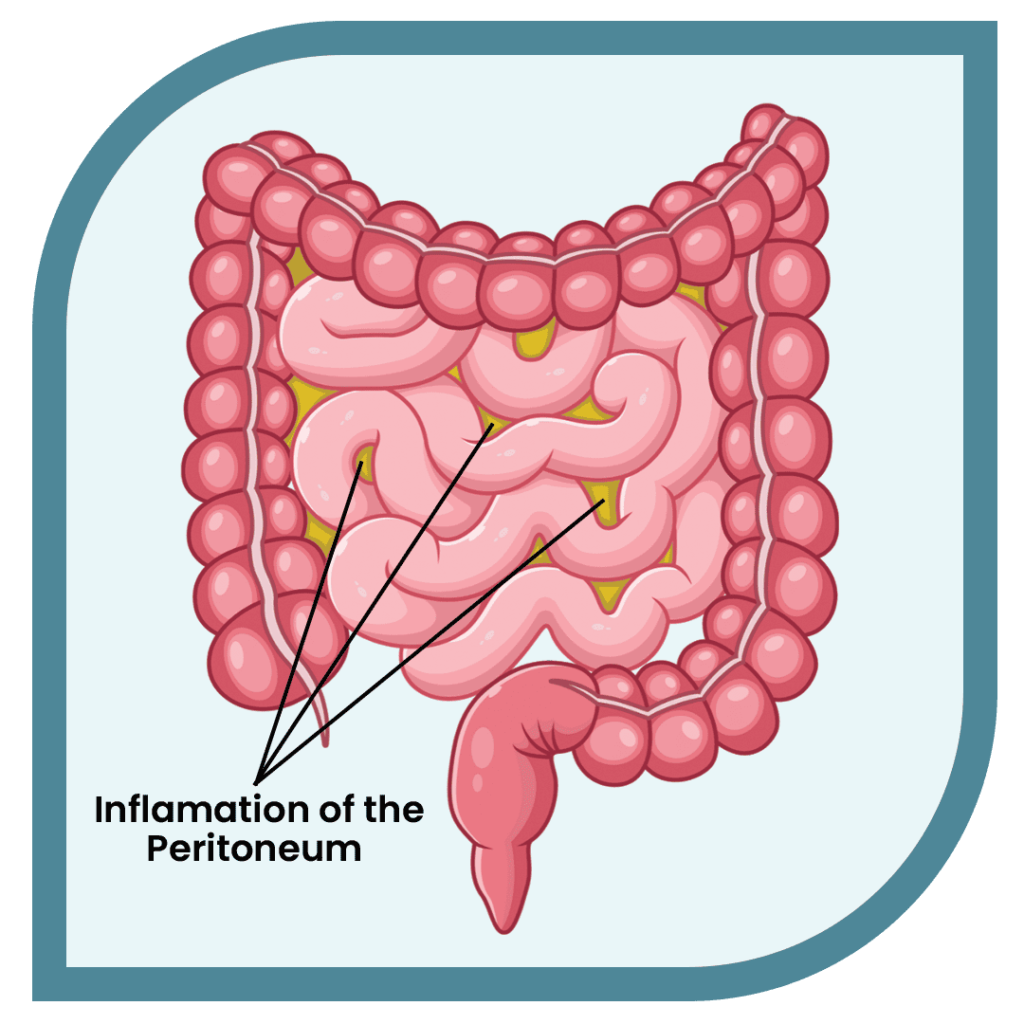
Pathogenesis of Peptostreptococcus Peritonitis
Peptostreptococcus species are commensals residing on mucocutaneous surfaces, including the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary system. Disruption of mucosal barriers—due to trauma, surgery, or disease—can facilitate their translocation into sterile body sites, culminating in infection. In the peritoneal cavity, these bacteria can proliferate, especially in environments with reduced oxygen tension, leading to peritonitis.
Clinical Manifestations
The clinical presentation of Peptostreptococcus peritonitis is often insidious, with symptoms that may include:
- Abdominal Pain: Typically diffuse and persistent.
- Fever: Reflecting systemic inflammatory response.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Resulting from gastrointestinal irritation.
- Altered Bowel Habits: Such as diarrhea or constipation.
In cases associated with peritoneal dialysis, cloudy dialysate is a hallmark sign. It’s noteworthy that Peptostreptococcus peritonitis can be complicated by bacteremia, potentially leading to metastatic infections like endocarditis or splenic infarction.6
Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis necessitates a combination of clinical suspicion and laboratory investigations:
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans can identify abscess formation or other intra-abdominal pathologies.
- Laboratory Tests: Elevated inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein, white blood cell count) support the diagnosis.
Treatment Strategies
Management of Peptostreptococcus peritonitis involves:
- Antimicrobial Therapy: Empirical broad-spectrum antibiotics with anaerobic coverage should be initiated promptly. Upon identification of Peptostreptococcus, therapy can be tailored based on susceptibility profiles.
- Source Control: Surgical intervention may be necessary to drain abscesses or address perforated viscus.
- Supportive Care: Maintenance of hemodynamic stability and organ function is crucial.
In peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis, catheter removal might be warranted in refractory cases.
Prevention and Prognosis
Preventive measures include:
- Aseptic Techniques: Especially during peritoneal dialysis to minimize infection risk.
- Prompt Treatment of Infections: Early management of mucosal infections can prevent translocation of bacteria.
The prognosis of Peptostreptococcus peritonitis varies, with outcomes dependent on timely diagnosis and appropriate management. Delayed treatment can lead to complications such as sepsis or chronic infection.