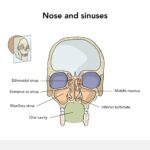
Acute Maxillary Sinusitis Induced by Moraxella catarrhalis, commonly referred to as a sinus infection, is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses—the air-filled cavities located within the cheekbones. This condition can be precipitated by various pathogens, with Moraxella catarrhalis being a notable bacterial contributor.
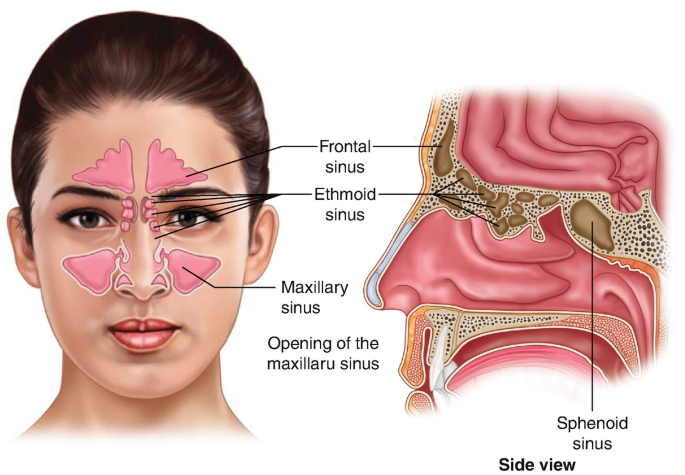
Understanding Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis is a gram-negative, aerobic diplococcus bacterium that predominantly inhabits the upper respiratory tract. It is a frequent cause of otitis media in children and acute and chronic sinusitis across all age groups.
Pathophysiology of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis Induced by Moraxella catarrhalis
The pathogenesis of acute maxillary sinusitis involves the obstruction of the sinus ostium, leading to mucus accumulation and bacterial proliferation. Moraxella catarrhalis can ascend from the nasopharynx to the sinuses, causing infection.
Clinical Manifestations
Patients with acute maxillary sinusitis may present with:
- Headache: Often localized over the affected sinus.
- Facial Pain or Pressure: Particularly over the cheekbones.
- Nasal Obstruction: Leading to difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Purulent Nasal Discharge: Thick, yellow or green mucus.
- Fever: Occasionally present, especially in bacterial infections.
- Dental Pain: Discomfort in the upper teeth due to sinus pressure.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, supported by imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scans to assess sinus involvement. Microbiological cultures can identify the causative organism, with Moraxella catarrhalis being a common pathogen.
Treatment Strategies
Management of acute maxillary sinusitis includes:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Empiric treatment with antibiotics effective against Moraxella catarrhalis, such as amoxicillin-clavulanate, is recommended.
- Symptomatic Relief: Use of nasal decongestants and saline irrigation to alleviate nasal congestion.
- Analgesics: Over-the-counter pain relievers to manage headache and facial pain.
- Corticosteroids: In certain cases, intranasal corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
Prevention and Prognosis
Preventive measures include good hygiene practices, smoking cessation, and managing underlying conditions like allergies. With appropriate treatment, the prognosis for acute maxillary sinusitis is generally favorable.
Understanding the role of Moraxella catarrhalis in acute maxillary sinusitis is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can lead to a favorable outcome and reduce the risk of complications.