Chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is a persistent and potentially debilitating condition affecting the middle ear. Characterized by chronic inflammation, tympanic membrane perforation, and recurrent or persistent ear discharge, CSOM primarily involves the tubotympanic compartment. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this condition.
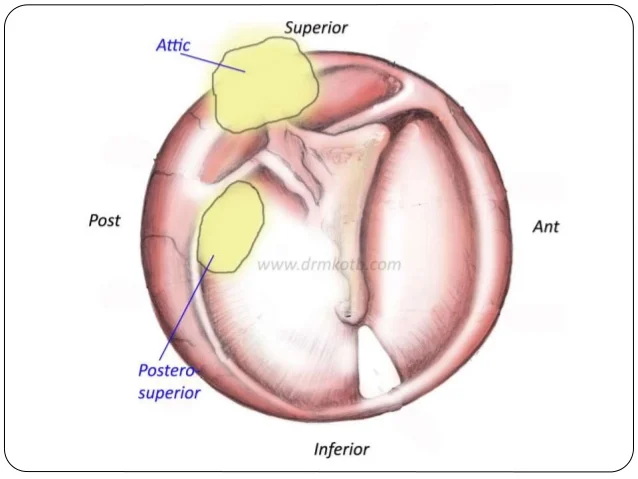
What Is Chronic Tubotympanic Suppurative Otitis Media?
Its a subtype of chronic otitis media confined to the anterior-inferior part of the middle ear cleft. It is typically associated with:
- A perforated tympanic membrane (eardrum).
- Non-marginal perforations.
- Recurrent or persistent mucopurulent ear discharge.
Unlike its counterpart, atticoantral otitis media, the tubotympanic type is not associated with cholesteatoma or severe bone destruction.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media:
1. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Impaired ventilation of the middle ear due to Eustachian tube dysfunction can lead to chronic inflammation and infection.
2. Infections
Recurring upper respiratory tract infections and untreated acute otitis media can predispose individuals to CSOM.
3. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
- Poor hygiene.
- Exposure to polluted water or swimming in contaminated water.
- Passive smoking.
4. Socioeconomic Status
Low socioeconomic conditions often correlate with inadequate access to healthcare, increasing the likelihood of untreated ear infections.
Clinical Presentation
The hallmark symptoms of chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media include:
- Persistent or recurrent ear discharge (otorrhea), often mucopurulent.
- Hearing loss, typically conductive in nature.
- A painless condition, except during secondary infections.
Additional signs include tympanic membrane perforation observed upon otoscopic examination and possible granulation tissue formation in the middle ear.
Diagnosis
1. Clinical History and Examination
A detailed history of symptoms, duration, and recurrence patterns is essential. Otoscopic examination reveals:
- Perforation in the pars tensa of the tympanic membrane.
- Active or inactive discharge.
2. Audiometry
Pure tone audiometry is used to assess the degree and type of hearing loss, often showing a conductive hearing loss pattern.
3. Microbiological Culture
A sample of ear discharge is sent for culture and sensitivity testing to identify causative organisms, which are often:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus aureus
4. Imaging
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the temporal bone may be required to rule out complications or assess mastoid involvement.
Treatment
1. Medical Management
The primary treatment of chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media involves:
- Topical Antibiotics: Ear drops containing quinolones or aminoglycosides are commonly prescribed.
- Aural Toilet: Regular cleaning of the ear canal to remove debris and discharge.
- Antiseptics: Topical antiseptic ear drops may be used to reduce bacterial load.
2. Surgical Intervention
For patients unresponsive to medical management, surgical options include:
- Myringoplasty: Surgical repair of the tympanic membrane to restore its integrity and prevent recurrence.
- Tympanoplasty: A combined procedure to repair the tympanic membrane and ossicular chain if necessary.
3. Management of Complications
Complications such as mastoiditis or intracranial infections require prompt and aggressive treatment, often involving mastoidectomy.
Complications
If untreated or inadequately managed, CSOM can lead to serious complications, including:
- Mastoiditis.
- Facial nerve paralysis.
- Intracranial infections (e.g., meningitis, brain abscess).
- Persistent hearing loss.
Prevention
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic tubotympanic suppurative otitis media:
- Prompt treatment of acute otitis media.
- Maintaining ear hygiene and avoiding water entry into the ear.
- Vaccination against common pathogens such as Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Avoidance of passive smoking and other environmental risk factors.