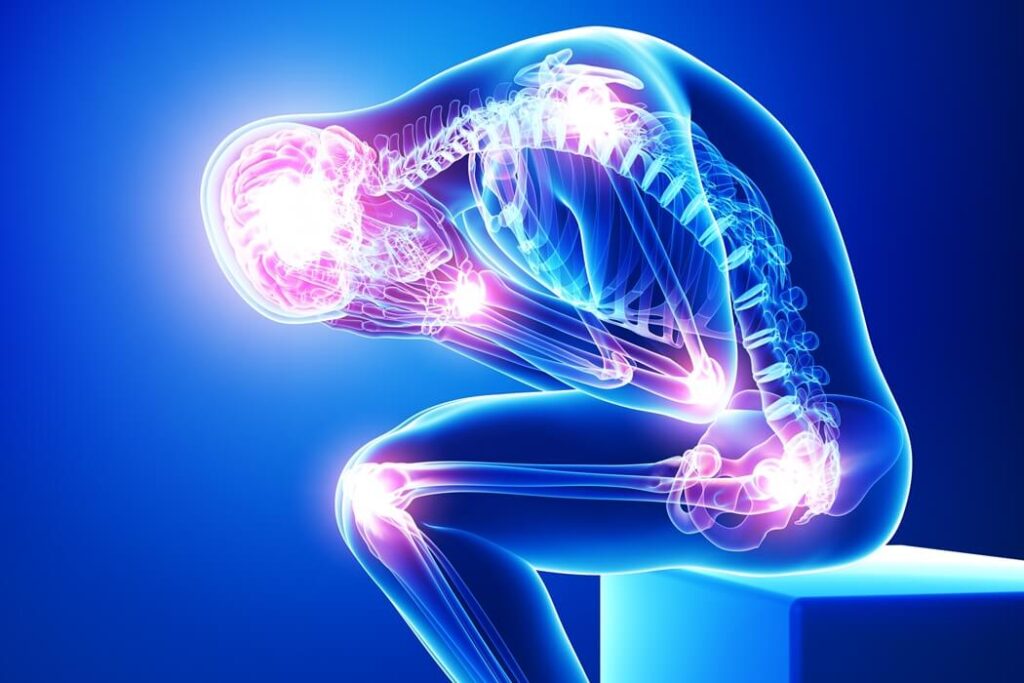
What Is Chronic Pain?
Chronic pain is a persistent and debilitating condition that lasts for more than three months, often resisting standard medical treatments. Unlike acute pain, which signals injury or illness, chronic pain may continue even after the original cause has resolved. It affects physical, emotional, and mental health, significantly impacting quality of life.
Key Characteristics of Chronic Pain:
- Duration of three months or more.
- Can be constant or intermittent.
- Often unresponsive to traditional pain relief methods.
Common Causes of Chronic Pain
Its can arise from various conditions, injuries, or illnesses. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Medical Conditions Associated with Chronic Pain:
- Arthritis: Inflammation in joints leading to persistent pain and stiffness.
- Fibromyalgia: Widespread muscle pain often accompanied by fatigue.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage causing burning or tingling sensations.
- Migraines: Intense, recurring headaches that can last for hours or days.
- Back Pain: Frequently caused by spinal issues such as herniated discs or scoliosis.
Lifestyle and Psychological Factors:
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Poor posture.
- Stress and anxiety.
Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic pain vary depending on the underlying cause and may include:
- Persistent aching, throbbing, or sharp sensations.
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances.
- Mood changes such as depression or irritability.
- Decreased mobility and flexibility.
- Cognitive issues like difficulty concentrating (often referred to as “brain fog”).
Diagnosing
Its requires a multi-faceted approach, as it often lacks visible signs. Doctors use a combination of the following methods:
- Medical History: Comprehensive review of symptoms and past conditions.
- Physical Exams: Identifying areas of tenderness or limited mobility.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, or X-rays to detect physical abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Rule out underlying conditions such as infections or autoimmune diseases.
Treatment Options
Effective management of chronic pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach, blending medical interventions with lifestyle changes.
Medications:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen, acetaminophen.
- Prescription Medications: Opioids, antidepressants, anticonvulsants.
- Topical Treatments: Creams or patches containing capsaicin or lidocaine.
Physical and Occupational Therapy:
- Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and posture.
- Ergonomic strategies to reduce strain during daily activities.
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Stimulates specific points to alleviate pain.
- Massage Therapy: Relieves tension in muscles and promotes relaxation.
- Chiropractic Care: Adjustments to improve spinal alignment.
Psychological Support:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addresses negative thought patterns associated with chronic pain.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Helps manage stress and pain perception.
Coping Strategies for Living with Chronic Pain
Living with chronic pain can be challenging, but adopting certain strategies can improve your overall well-being.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga.
- Balanced Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish.
- Adequate Sleep: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a restful environment.
Building a Support System:
- Connect with family and friends.
- Join support groups or online communities for shared experiences and advice.
Stress Management Techniques:
- Practice deep breathing exercises.
- Engage in hobbies or activities that bring joy.
- Consider journaling to express emotions and track pain levels.
When to Seek Professional Help
While self-management strategies can be effective, there are times when professional help is essential:
- Pain persists or worsens despite home remedies.
- Difficulty performing daily activities.
- Symptoms of depression or anxiety appear.
- Side effects from medications are unmanageable.
Early intervention can improve outcomes and enhance quality of life.