Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition characterized by airflow obstruction, which makes breathing difficult. Bronchospasms, or the sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchi, often accompany COPD. This condition exacerbates respiratory distress and can significantly impair a patient’s quality of life. COPD with bronchospasms requires a multifaceted approach to diagnosis, management, and treatment.
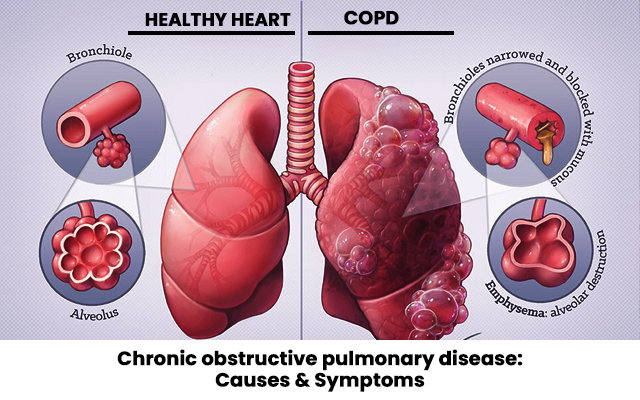
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing difficulties. The two most common conditions under the COPD umbrella are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions typically result from prolonged exposure to harmful substances, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational dust.
Symptoms of COPD
COPD presents with several characteristic symptoms, including:
- Persistent cough, often referred to as a “smoker’s cough”
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion
- Wheezing and chest tightness
- Increased mucus production
- Frequent respiratory infections
The symptoms tend to worsen over time, especially if the underlying causes are not addressed.
Understanding Bronchospasms in COPD
Bronchospasms are episodes in which the muscles surrounding the bronchi (the air passages in the lungs) tighten, causing the airways to narrow. This constriction leads to difficulty in breathing and is often associated with wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Causes of Bronchospasms in COPD
Bronchospasms can be triggered by several factors in individuals with COPD, including:
- Exposure to irritants: Air pollution, dust, and tobacco smoke are common environmental triggers.
- Respiratory infections: Viral or bacterial infections can exacerbate bronchospasms in COPD patients.
- Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, or mold can trigger bronchial constriction.
- Cold air or sudden changes in temperature: These can cause the airways to constrict.
- Physical activity: Intense physical exertion may lead to breathing difficulties and spasms in the bronchi.
The Link Between COPD and Bronchospasms
Bronchospasms are particularly concerning for people with COPD because they add an additional layer of complexity to an already compromised respiratory system. The narrowing of the airways due to bronchospasms limits airflow, which may cause a severe reduction in oxygen levels, leading to shortness of breath and other complications.
Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis of COPD with bronchospasms involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. These steps ensure that the severity of the condition is assessed, and the appropriate treatment plan is created.
Medical History
The physician will inquire about:
- Symptom history: Duration, frequency, and intensity of cough, shortness of breath, and wheezing.
- Risk factors: Smoking history, exposure to environmental pollutants, and family history of lung diseases.
- Comorbidities: Conditions like heart disease or diabetes that may exacerbate COPD symptoms.
Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will listen to the lungs for abnormal sounds, such as wheezing, crackles, or decreased breath sounds, which indicate airflow obstruction.
Diagnostic Tests
- Spirometry: This is the most common test for diagnosing COPD. It measures lung function and the amount of air a person can inhale and exhale.
- Chest X-rays: A chest X-ray can help detect lung abnormalities, such as emphysema.
- CT Scan: A more detailed imaging tool that can provide insights into lung tissue damage and the extent of bronchial constriction.
Treatment Options for COPD with Bronchospasms
Effective management of COPD with bronchospasms aims to reduce symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve quality of life. Treatment strategies include medications, lifestyle changes, and therapeutic interventions.
Medications
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles around the airways, easing the bronchospasm. Common bronchodilators include:
- Short-acting beta-agonists (SABA): Used as rescue medications for acute symptoms.
- Long-acting beta-agonists (LABA): Used for long-term management of symptoms.
- Anticholinergics: Help relax the airway muscles and reduce mucus production.
- Inhaled Steroids: These drugs reduce inflammation in the airways, which helps prevent bronchospasms.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors: These medications reduce inflammation and relax the airways in severe COPD cases.
Oxygen Therapy
For patients with severe COPD and low oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen therapy may be necessary. This ensures that the body receives sufficient oxygen to support vital organs.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are designed to improve physical fitness and teach patients how to manage breathing difficulties. These programs often include:
- Exercise training
- Breathing techniques
- Education on lifestyle changes
Lifestyle Modifications
- Smoking cessation: The most crucial step in managing COPD is quitting smoking, as it is the leading cause of the disease.
- Dietary changes: A healthy, balanced diet can help improve lung function and overall health.
- Avoiding triggers: Staying away from allergens, irritants, and pollutants can prevent exacerbations and bronchospasms.
Managing Bronchospasms in COPD
Managing bronchospasms involves a combination of medication and lifestyle strategies aimed at minimizing triggers and improving airflow. The use of quick-relief inhalers (such as short-acting bronchodilators) during an episode of bronchospasm can provide rapid symptom relief.
Preventive Measures
- Environmental control: Avoid exposure to pollutants, allergens, and irritants.
- Vaccinations: Annual flu vaccines and pneumococcal vaccines help prevent infections that could trigger bronchospasms.
- Regular check-ups: Routine visits to the healthcare provider can help monitor disease progression and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Prognosis and Living with COPD with Bronchospasms
While COPD with bronchospasms is a chronic condition with no known cure, effective management can significantly improve quality of life. With the right treatment plan, patients can maintain an active lifestyle, reduce the frequency of exacerbations, and minimize the severity of symptoms.
Impact on Quality of Life
People living with COPD and bronchospasms often face challenges such as:
- Physical limitations: Shortness of breath may prevent individuals from performing daily tasks.
- Mental health concerns: The ongoing nature of COPD can contribute to feelings of anxiety and depression.
- Social isolation: Limited physical capabilities may lead to social withdrawal and reduced interaction with others.